Figure 1.
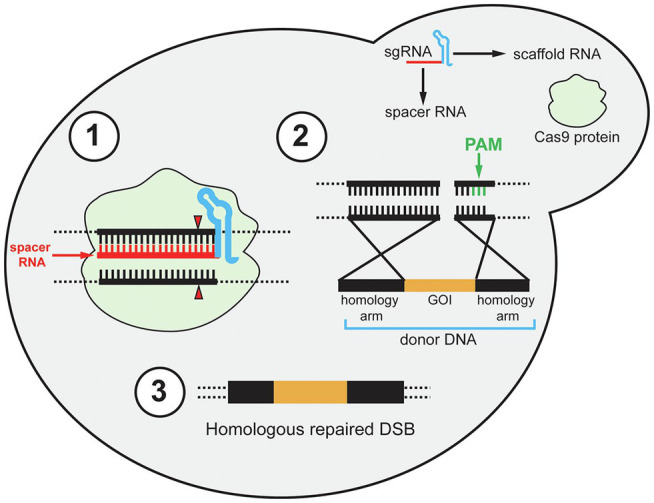
Schematic diagram of the CRISPR/Cas9 mechanism in yeast. The single gRNA (sgRNA) contains two components: scaffold RNA (tracrRNA and structural part of crRNA) and a 20-nt spacer RNA. (1) After the Cas9 protein binds to the sgRNA, Cas9 binds to the target sites in the genomic DNA and undergoes conformational change to cut both strands of the target site 3-bp upstream of the PAM site (red triangle). PAM site is shown in step 2. (2) After a double-stranded break (DSB) is induced, the preferable homology-directed repair (HDR) mechanism repairs the DSB using donor DNA. The donor DNA contains 5' and 3' homology arms and a gene of interest (GOI). The GOI can be non-functional for gene deletion purposes. Note that although the PAM site is emphasized in the second step (green bars), the PAM site is required for Cas9-gRNA complex to recognize the target sites in the first step. (3) After HDR, the DSB is repaired and the GOI is integrated.
