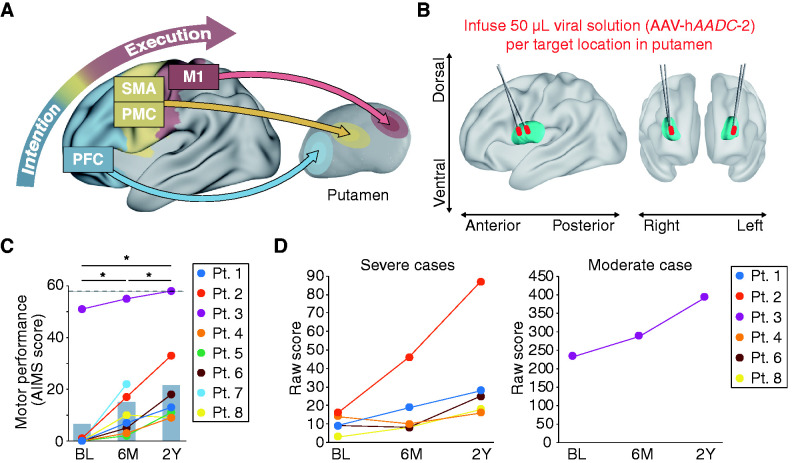
Figure 1.
Gene therapy for aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency. (A) Conceptual model of the cortico-putaminal network in the motor system. (B) 3D model of the putamen and infusion tracks defined from a postoperative T2-weighted MR image (see Supplementary Fig. 1). (C) Gross motor performance scored by AIMS increased from the baseline to 2Y post-treatment. Dashed line: The maximum score of AIMS; BL: baseline; Pt: patient. (D) Cognition–adaptation score of the Kyoto Scale of Psychological Development showed the acquisition of new motor skills including voluntary arm extension, grabbing and holding objects, after the gene therapy. Grabbing and holding objects is recognized from 10 points, and arm extension to grab objects is recognized from 16 points.