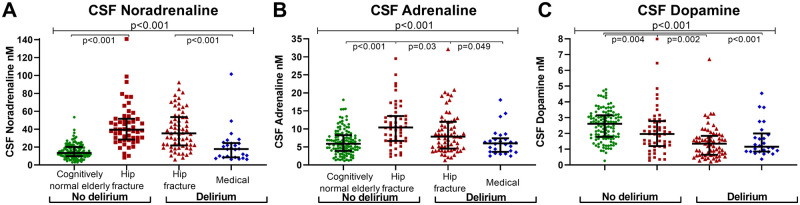
Figure 2.
CSF catecholamine levels in patients with and without delirium in all cohorts. (A) CSF noradrenaline levels and (B) CSF adrenaline levels were higher among the hip fracture patients (all, n = 118) while (C) CSF dopamine levels were highest among the cognitively normal elderly (n = 122). Furthermore, hip fracture patients with delirium (n = 65) had compared those with no delirium (n = 52) (B) lower CSF adrenaline levels and (C) lower CSF dopamine levels. Medical delirium patients (n=26) also had lower CSF dopamine relative to the cognitively normal elderly. Larger and smaller lines represent median and interquartile range, respectively. Two-tailed P-values for comparison of two groups are obtained by Mann–Whitney U-test. Differences in the three cohorts (upper line) were analysed by Kruskal–Wallis test.