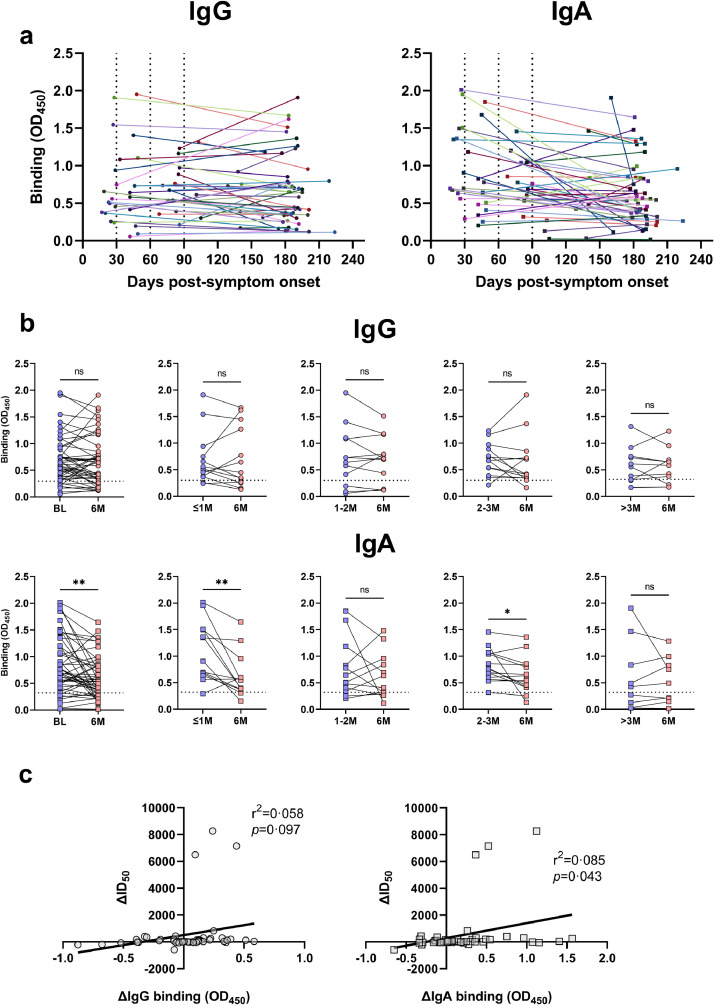
Fig. 5.
Longitudinal total binding (OD450) of IgG and IgA to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein of 48 mild COVID-19 subjects. A) Total IgG binding (left) and IgA binding (right) between all baseline and 6-month time points, with each colour/shade representing a different subject. Each dotted line on the X-axis represents the time post-symptom onset stratification, as described in the Figure 1 legend. B) Comparisons of total binding IgG (top) and IgA (bottom) values between baseline (BL; blue) and 6-month (6M; red) timepoints in all subjects (Paired-parametric T tests) and in stratified groups (Wilcoxon T tests). Baseline (BL) and 6-month (6M) timepoints were significantly different for IgA (**p=0•0019). For the stratified groups, ≤1M and 2-3M were significantly higher than their 6M timepoint for IgA (**p=0•0051, *p=0•039). No other comparisons were statistically significant (ns; p>0•05). C) Correlation of the change in 50% inhibitory dilution neutralising titres (ID50) against SARS-CoV-2 to the change in IgG (left; circles; r2=0•058, p=0•097; simple linear regression analysis) and IgA (right; squares; r2=0•085, p=0•043; simple linear regression analysis) binding.