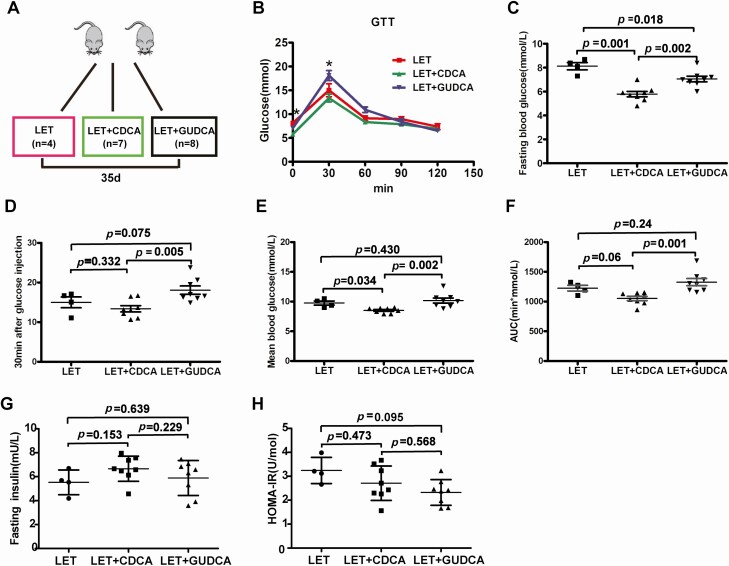
Figure 8.
Intestinal FXR plays an important role in glucose metabolism in PCOS model mice. Mice were divided into 3 groups (LET, LET+CDCA, and LET+GUDCA) and were treated for 35 days to explore the effects of intestinal FXR (LET: 4, LET+CDCA: 7, and LET+GUDCA: 8). (A) Schematic representation of the experimental design. (B) GTT. (C) Fasting blood glucose. (D) Thirty minutes after glucose injection. (E) Mean blood glucose. (F) Area under the curve (AUC) of the GTT. (G) Fasting insulin. (H) HOMA-IR. (B-H) P values were determined by 1-way ANOVA with the least significant difference (LSD) multiple comparison post hoc test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; GTT, glucose tolerance test; GUDCA, glycoursodeoxycholic acid; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance index; LET, letrozole; PCOS, polycystic ovarian syndrome.