Figure 2. Pallidum Volume Does Not Mediate the Association Between VO2max and Cognitive Performance.
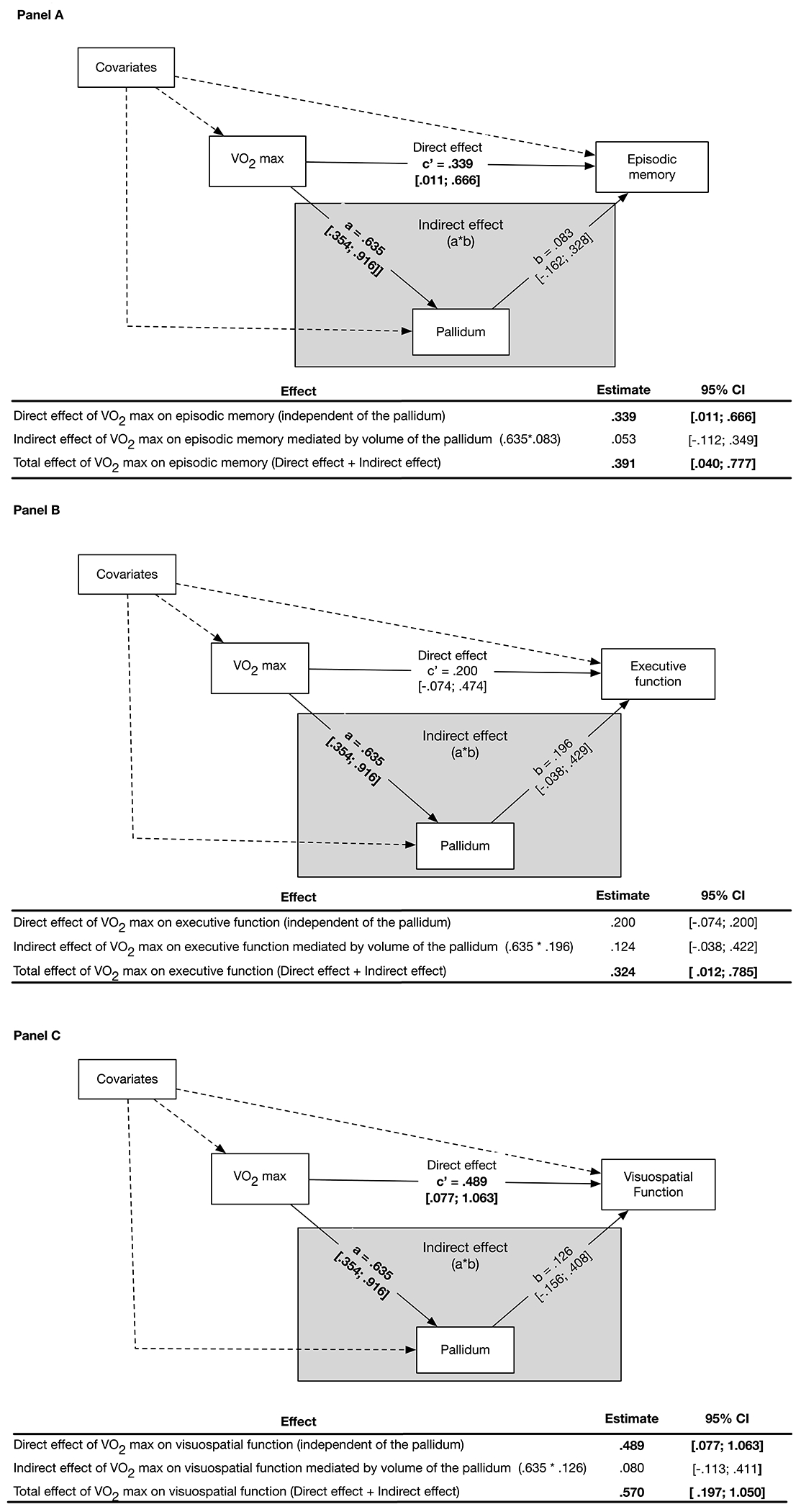
Panel A illustrates the structural equation mediation model with parameter Effects, Estimates, and 95% Confidence Intervals (CI). Pallidum volume does not significantly mediate the association between VO2max and episodic memory, as demonstrated by the non-significant Indirect effect (grey box) of the pallidum on this association. The Indirect effect is the product of the effect of VO2max on the pallidum volume (Path a) and the effect of pallidum volume on episodic memory (Path b). The Direct effect (Path c) is significant and is defined as the effect of VO2max on episodic memory while adjusting for the effect of pallidum volume and covariates. The total effect of VO2max on episodic memory is significant and is calculated by adding the Direct and Indirect effects. Episodic memory is a composite of the total number of correct words recalled on the immediate and long-delay free recall trials from the California Verbal Learning Test-II, and visual reproduction one and two scores from the Wechsler Memory Scales. Panel B illustrates a similar structural equation mediation model as in Panel A and demonstrates that pallidum volume is not a significant mediator (Indirect effect, grey box) of VO2max on executive function. The total effect of VO2max on executive function is significant. Executive function is a composite of the number of seconds to complete the inhibition and inhibition-switching subtests of the D-KEFS Color-Word Interference test, the number of errors on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test, total number of correct words on the switching fluency subtest from the D-KEFS Verbal Fluency test, and the total move score on the Tower of London-Drexel University test. Panel C illustrates a similar structural equation mediation model as in Panel A and demonstrates that pallidum volume is not a significant mediator (Indirect effect, grey box) of the association between VO2max on visuospatial function. The Direct effect of VO2max on visuospatial function is significant. The total effect of VO2max on visuospatial function is significant. Visuospatial function is a composite score of visuospatial ability consisting of the Judgement of Line Orientation and Hooper Visual Organization Test. All parameter effect estimates were adjusted for covariates. Dashed pathways represent effects of covariates bolded estimates are significant at p < .05. The 95% confidence intervals for parameter estimates are presented in brackets.
