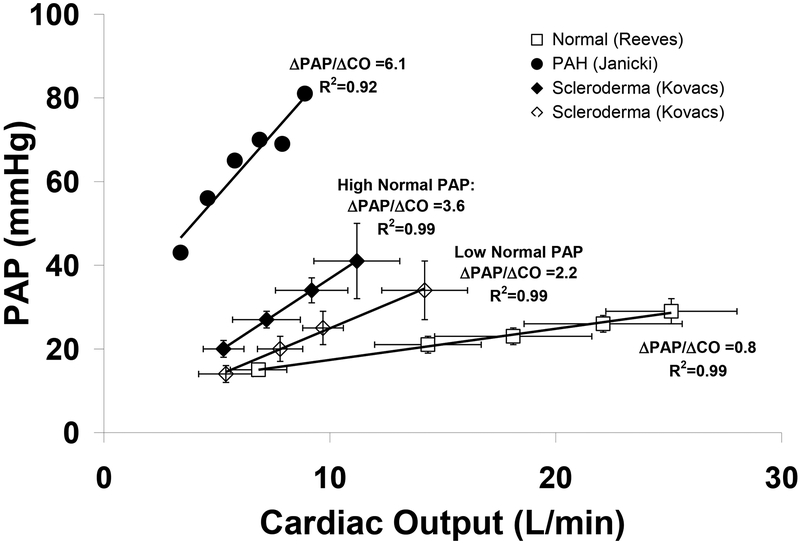
Figure 1.
Pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP)-flow relationships based on serial measurements of mean PAP and cardiac output during incremental exercise. Normal subjects (□), patients with scleroderma with PAP in the lower normal range (◊) and upper normal range (♦), and patients with resting PAH (•) demonstrate approximately linear pressure-flow responses during exercise with progressively higher ΔPAP/ΔCO that may be indicative of early pulmonary vasculopathy in the scleroderma groups. Adapted with permission from (□) Reeves,35 Kovacs (◊,♦),54 and (•)Janicki.13