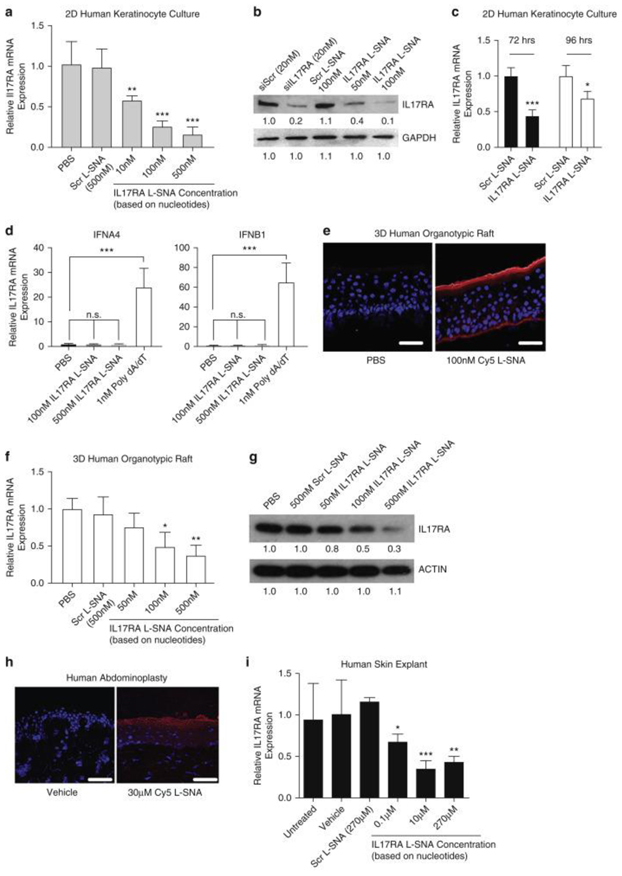
Figure 3. IL17RA L-SNA knocks down IL17RA expression in human cultures, rafts, and explants.
(a, b) NHEKs were treated and harvested after 48 hrs for qRT-PCR (a) and western blots (b; siIL17RA is free small interfering RNA). (c) IL17RA knockdown in proliferating NHEKs through 96 hrs. (d) qRT-PCR of NHEK IFNA4 and IFNB1 after 24 hrs treatment with 100 nM or 500 nM IL17RA L-SNA or 1 nM poly dA/dT. (e) Immunofluorescence microscopy of 3D rafts 48 hrs after 100 nM Cy5-L-SNA application. Bars = 50μm. (f, g) IL17RA knockdown 48 hrs after 3D raft treatment. (h) Immunofluorescence microscopy 24 hrs after 30μM Cy5 L-SNA application to human explants. Bars = 50μm. (i) Dose-dependent IL17RA knockdown 24 hrs after human explant treatment. Values mean ± standard error of the mean. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Red, Cy5 L-SNA; Blue, DAPI. 2D, 2-dimensional; 3D, 3-dimensional; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; hrs, hours; IL17RA, IL-17A receptor; IL17RA L-SNA, IL-17A receptor liposomal spherical nucleic acid; L-SNA, liposomal spherical nucleic acid; NHEK, normal human epidermal keratinocytes; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase–PCR; Scr L-SNA, scrambled liposomal spherical nucleic acid; siIL17RA, small interfering IL-17A receptor; siScr, small interfering scrambled.