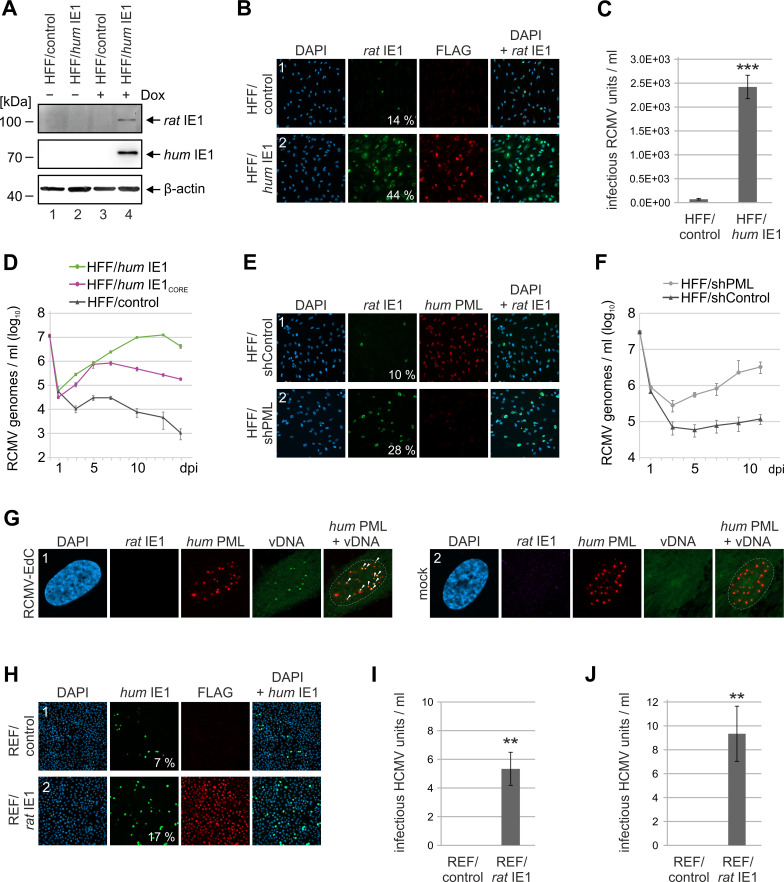
Fig 8. RCMV replication in human fibroblasts expressing humIE1.
(A, B) Increased initiation of RCMV gene expression in humIE1-expressing HFF. HFF with doxycycline-inducible expression of FLAG-tagged humIE1 (HFF/humIE1) or control cells (HFF/control) were treated with doxycycline (+ Dox) or mock treated (- Dox) for 24 h and subsequently infected with RCMV-E (MOI = 0.1). At 8 h post-infection (hpi), cells were harvested for Western Blot analysis of ratIE1 as well as humIE1 with an anti-FLAG antibody and β-actin as loading control (A) or for immunofluorescence detection of ratIE1, humIE1 (FLAG), and cell nuclei by DAPI staining (B). The percentage of rat IE1-positive cells was determined from triplicate samples. (C) Release of infectious RCMV particles from humIE1-expressing HFF. HFF/control and HFF/humIE1 were infected with RCMV-E at an MOI of 0.01 after 24 h of doxycycline treatment. Supernatants were harvested at 6 d post infection and titrated on REF cells. Values are derived from triplicate samples and represent mean values ± SD. P-values were calculated using two-tailed Student’s t-test. ***, p ≤ 0.001. (D) Multistep growth curve analysis of RCMV in humIE1-expressing HFF. HFF/control, HFF/humIE1 and HFF/humIE1CORE, which express residues 1–382 of humIE1, were treated with doxycycline for 24 h and subsequently infected with RCMV-E at an MOI of 0.01. Supernatants were harvested at indicated times after infection and analyzed for genome equivalents by RCMV gB-specific quantitative real-time PCR. (E) Increased initiation of RCMV gene expression in PML-depleted human fibroblasts. HFF expressing a control shRNA (HFF/shControl) or a shRNA directed against PML (HFF/shPML) were infected with RCMV-E (MOI = 0.1). At 8 hpi, cells were fixed for immunofluorescence detection of ratIE1 and humPML. Cell nuclei were visualized by DAPI staining. The percentage of ratIE1-positive cells was quantified from triplicate samples. (F) Multistep growth curve analysis of RCMV in PML-knockdown HFF. HFF/shControl and HFF/shPML infected with RCMV-E at an MOI of 0.01. Supernatants were harvested at indicated times after infection and analyzed for genome equivalents by RCMV gB-specific quantitative real-time PCR. (G) Colocalization of RCMV genomes with PML-NBs in human fibroblasts. HFF cells were infected with RCMV-EdC at an MOI of 0.05 or were mock infected. At 8 hpi, cells were fixed for click labeling to visualize RCMV genomes (vDNA) in combination with immunofluorescence detection of ratIE1 and humPML. DAPI staining was performed to visualize cell nuclei. Arrows in the merged PML-vDNA image indicate RCMV genomes colocalizing with PML-NBs. Dashed lines indicate the position of the cell nuclei. (H) Increased initiation of HCMV gene expression in ratIE1-expressing REF. REF/control and REF/ratIE1 were treated with doxycycline for 24 h and subsequently infected with HCMV strain AD169 (MOI = 0.1). At 24 hpi, cells were harvested for immunofluorescence analysis of humIE1, followed by quantification of humIE1-positive cells from triplicate samples. RatIE1 expression was confirmed by staining with an anti-FLAG antibody and cell nuclei were detected with DAPI. (I, J) Release of infectious HCMV particles from ratIE1-expressing REF. REF/control and REF/ratIE1 were treated with doxycycline for 24h and subsequently infected with HCMV strain AD169 (I) or TB40/E (J) at an MOI of 0.1. Supernatants were harvested at 6 d post infection and directly subjected to titration on HFF cells. Values are derived from triplicate samples and represent mean values ± SD. P-values were calculated using two-tailed Student’s t-test. **, p ≤ 0.01.