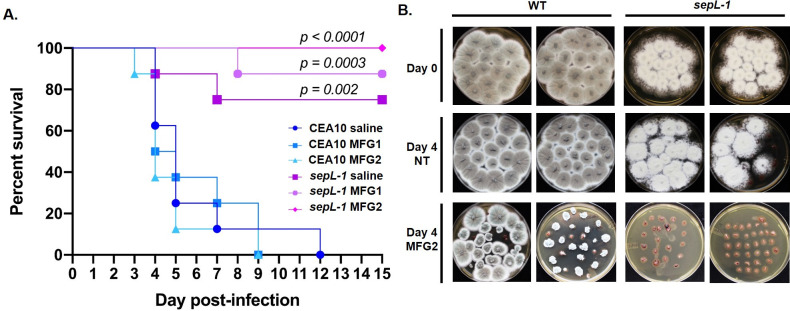
Fig 10. Loss of hyphal septation improves echinocandin therapy characterized by clearance of fungal burden from lung tissue.
A) Survival analysis of mice infected with either the CEA10 or sepL-1 mutant strain with and without micafungin therapy. All mice were immune suppressed through intraperitoneal injection of cyclophosphamide on days -3, +1, +4, and +7 and a single subcutaneous injection of triamcinolone acetonide on day -1. Mice were inoculated with 1 X 106 conidia of the indicated strain suspended in 20 μl of sterile saline on day 0 and then received three separate intraperitoneal injections of micafungin at either 1 mg/kg (MFG1) or 2 mg/kg (MFG2) on days +1, +2 and +3. Statistical comparisons were made by Mantel-Cox log-rank test and represent each sepL-1 mutant experimental arm compared to its CEA10 control (i.e., CEA10 saline vs. sepL-1 saline, CEA10 MFG1 vs. sepL-1 MFG1, and CEA10 MFG2 vs. sepL-1 MFG2). B) CEA10 and sepL-1 residual lung tissue burden at day 0 and day 4 with and without micafungin 2 mg/kg therapy. Organ cultures are shown from two representative animals from each treatment group. Note that the sepL-1 infected mice treated with micafungin 2 mg/kg are culture negative at day 4 post-inoculation. MFG = micafungin.