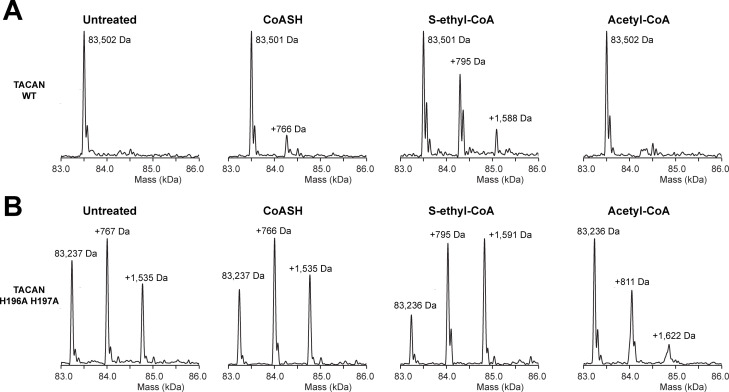
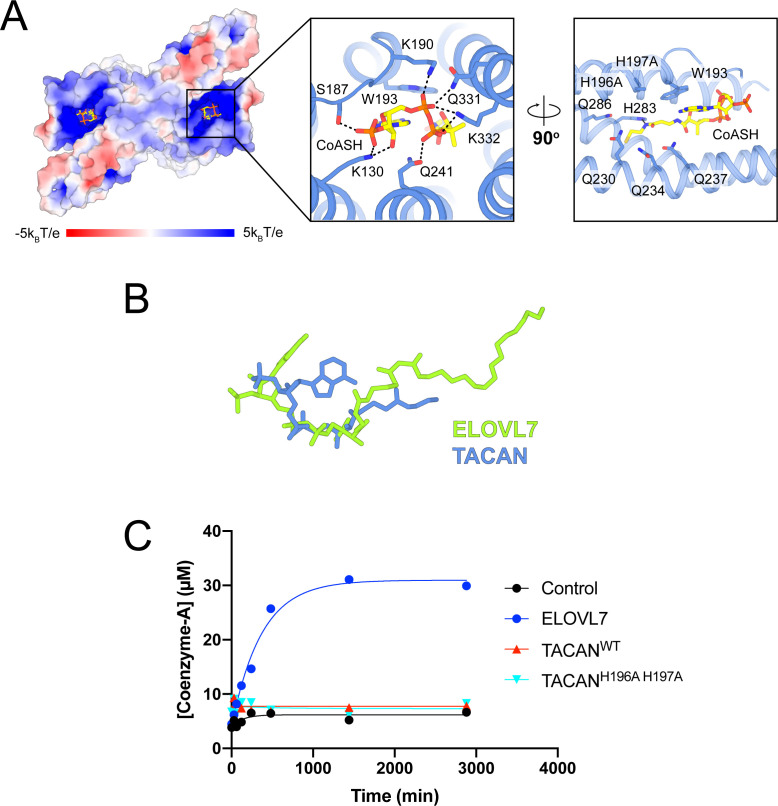
(
A) Binding details of CoASH in TACAN
H196A H197A. Surface charge is represented from blue (positive charges) to red (negative charges). Neighboring residues are shown as sticks, and the hydrogen bonding is indicated by a black dash. A CoASH molecule is shown as sticks and colored according to atom type. (
B) Conformation comparison of eicosanol-CoA in ELOVL7 (green) and CoASH in TACAN (blue) based on the alignment in
Figure 4A. (
C) CoASH releasing activity of ELOVL7 and TACAN. Proteoliposomes of TACAN and ELOVL7 reconstituted in soy L-α-phosphatidylcholine (soy-PC) at 1:50 protein-to-lipid ratio (w/w) with 10 μg protein and 500 μg soy-PC were used. Empty proteoliposomes made of soy-PC were used as control. ELOVL7 showed significant activity, while neither the wild-type nor His196Ala His197Ala mutant of TACAN showed any activity.