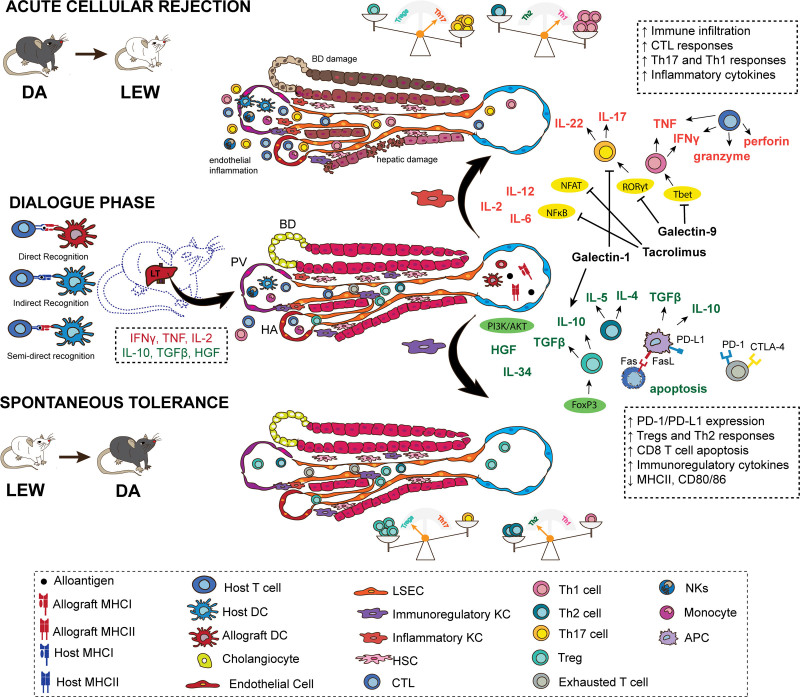
FIGURE 2.
The days that follow an LT are marked by a dialogue between the liver graft and the host, through direct, indirect, and semidirect allorecognition. In this process of getting acquainted, the communication between different cells and the signals in the microenvironment of the liver will determine whether tolerance or rejection will follow. An initial inflammatory response, marked by IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF, and VCAM-1, leads to intragraft leukocyte infiltration independent of the final outcome and, in the presence of hepatic signals, is key to prime the response seen afterward. For instance, IFN-γ secretion is key to upregulate PD-L1 expression by LSECs, hepatocytes, and KCs, which subsequently contributes to the establishment of a tolerogenic environment. If, however, the alloantigen load or inflammatory signals, such as IL-2, are overexpressed, then the response is skewed toward acute cellular rejection. KCs are found in a spectrum from anti-inflammatory to proinflammatory phenotypes and are important contributors to the final outcome following LT. Activation of transcription factors, such as NF-κB, NFAT, RORγt, T-bet, leads to an environment enriched in proinflammatory cytokines and guide T-cell differentiation toward Th17 and Th1 responses. On the other hand, the engagement of PIK3/AKT and the upregulation of coinhibitory molecules, such as PD-L1, lead to a tolerogenic environment, with predominance of Treg and Th2 responses. APC, antigen-presenting cell; BD, bile duct; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated protein 4; DA, Dark Agouti; DC, dendritic cell; FasL, Fas ligand; FGL2, higher fibrinogen protein 2; FOXP3, forkhead box P3, HA, hepatic artery; HGF, hepatic growth factor; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; IFN-γ, interferon γ; KC, Kupffer cell; LEW, Lewis; LSEC, liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; LT, liver transplant; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; NF-κB, kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; NK, natural killer; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, PD-1 ligand; PV, portal vein; RORγt, retinoic acid receptor (RAR)–related orphan receptor (ROR)γt transcription factor; T-bet, T-box transcription factor; TGF-β, tumor growth factor β; Th, T helper cell; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; Treg, regulatory T cells; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.