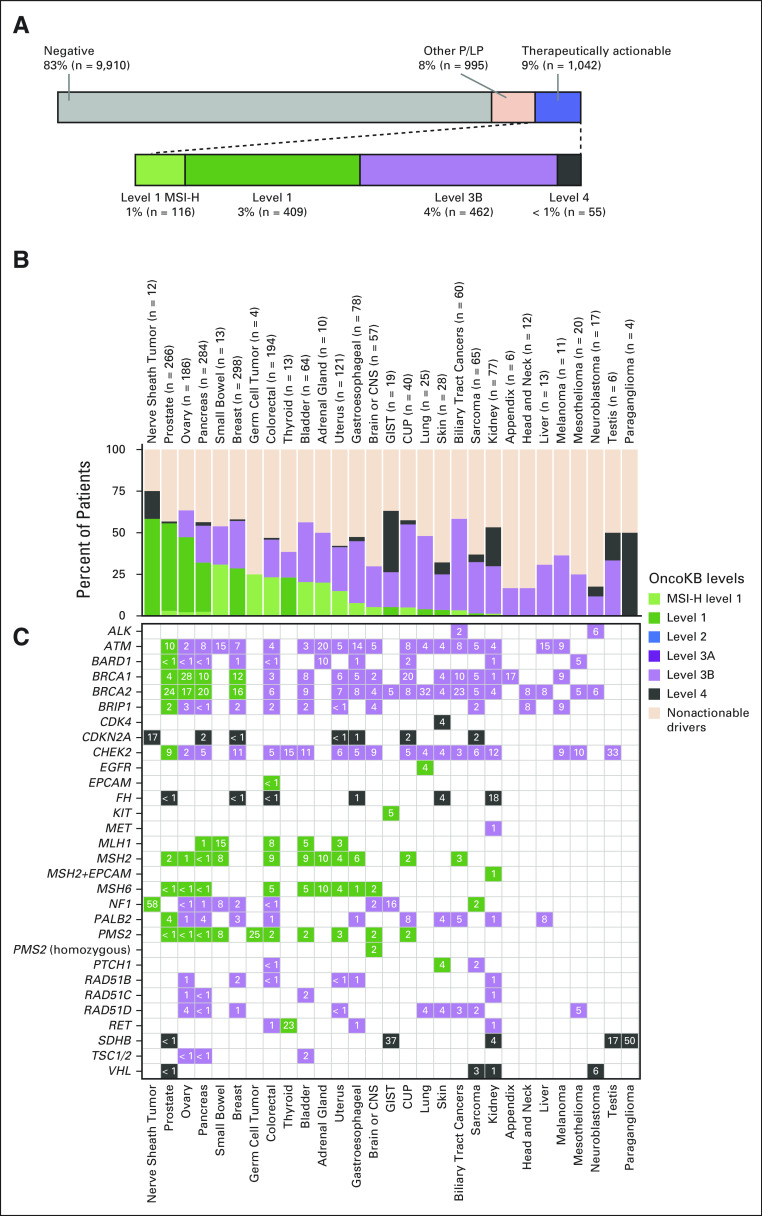
FIG 1.
Prevalence of germline variants with therapeutic actionability as classified by OncoKB. (A) Top panel, percent of 11,947 cancer patients with LP/P germline alterations considered therapeutically actionable by OncoKB (blue). Lower panel, breakdown of therapeutically actionable germline alterations by OncoKB level of evidence. Level 1 MSI-H (light green) indicates patients with germline LP/P alterations in the DNA mismatch repair genes whose tumors also exhibit MSI-H/dMMR. In (B and C), highest OncoKB level of evidence by cancer type and gene is shown (28 cancer types shown). (B) In the stacked bar graph, columns indicate tumor type. Number of patients with LP/P alterations per cancer type specified in labels on top x-axis. Each bar is broken down by percentage of patients harboring a germline alteration with color-indicated level of evidence or nonactionable P/LP alteration (light orange). (C) In the frequency map, rows indicate germline gene alteration present in patients and numbers indicate the percentage of patients per cancer type that harbors an alteration in each gene. CUP, cancer of unknown primary; dMMR, defective DNA mismatch repair; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor; LP/P, likely pathogenic or pathogenic, MSI-H, high-frequency microsatellite instability.