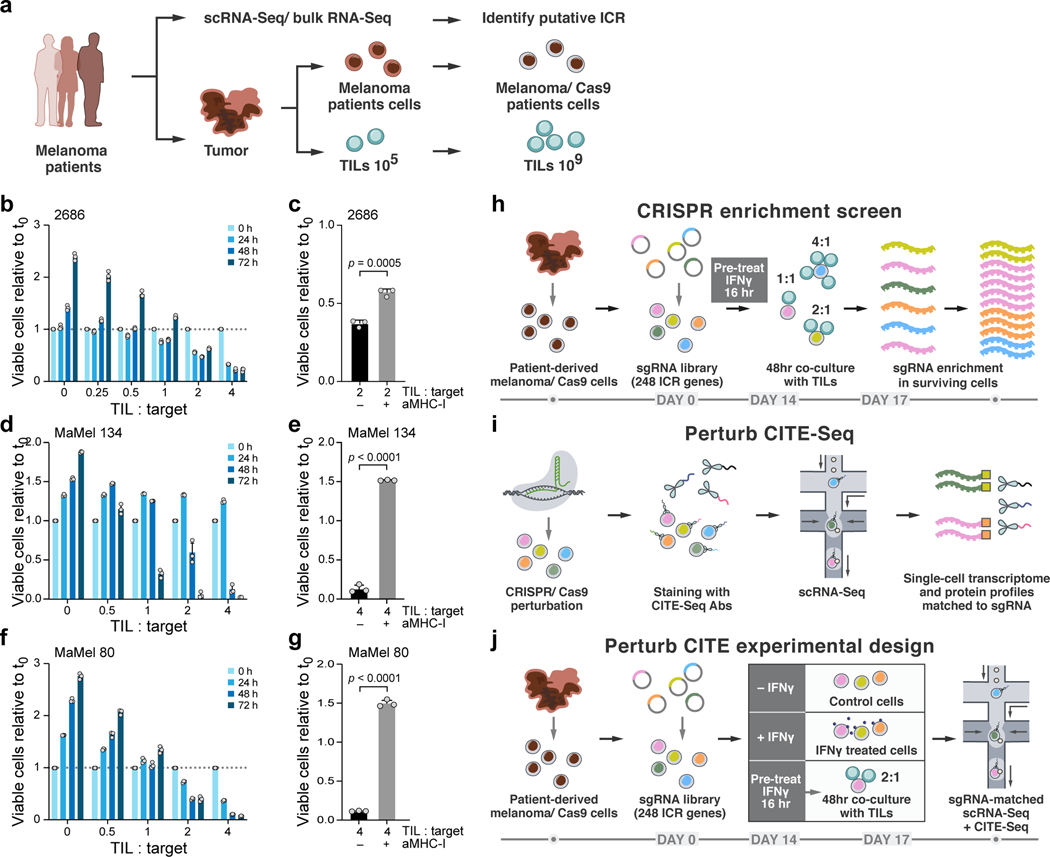
Figure 1. Perturb-CITE-Seq to study tumor intrinsic mechanisms of T cell resistance using patient derived co-culture models.
a. Patient derived cell models and programs. Resected melanomas (left) were profiled by bulk and scRNA-seq (top) to identify an immune resistance program (ICR)9. Melanoma (brown, middle) and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs, blue, bottom) cells were grown from patients’ tumors; melanoma cells were transduced to express Cas9 and TILs were expanded to yield sufficient numbers for screening (Methods). b-g. Optimization and validation of co-culture system for TIL mediated killing of melanoma cells. b,d,f. Time and dose-dependent killing of melanoma target cells by autologous TILs in three patient derived co-culture models. Ratio of viable cancer cells (y axis, relative to t0) at different TIL : cancer cell ratios (x axis) at different time points (color legend) after pre-treatment of target cells with 1 ng/ml IFNγ for 16 hours using TILs without prior restimulation in each patient-derived co-culture model (panels). Experiment was performed in triplicates in each of two independent experiments. c,e,g. Target cell killing depends on MHC-I. Ratio of viable cancer cells (y axis, relative to t0) after 48 hours in a 4:1 TIL and cancer cell co-culture with cancer cells pre-treated with 1ng/ml IFNγ for 16 hours and TILs without prior restimulation, in the absence or presence of MHC-I blocking antibodies (x axis). Two-sided t-test. Error bars: Mean ±SD. Experiment was performed in triplicates in each of two independent experiments. h. Viability screen design. i. Perturb-CITE-Seq approach. j. Perturb-CITE-Seq screens to characterize regulators of melanoma immune evasion.