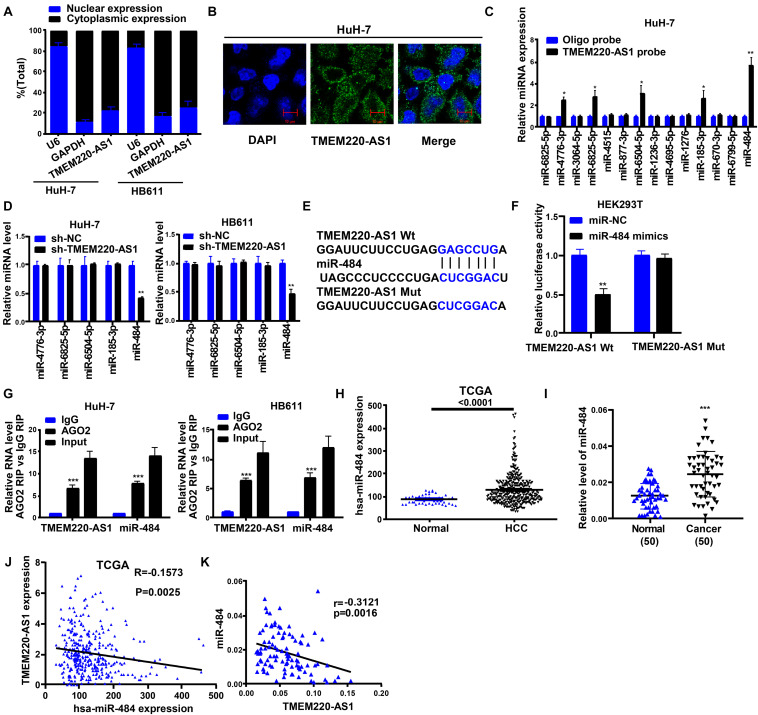
FIGURE 4.
TMEM220-AS1 is targeted by miR-484. (A,B) Localization of TMEM220-AS1 by nucleocytoplasmic separation experiment and RNA-FISH in HCC cells (bar = 10 μm). (C) The relative expression of candidate miRNAs which could potentially bind to TMEM220-AS1 were quantified by qRT-PCR after the biotinylated- TMEM220-AS1 pull-down assays in HuH-7 cells. (D) The levels of miRNAs after TMEM220-AS1 cutdown were tested by qRT-PCR. (E) Putative miR-484 binding sequence and mutation sequence of TMEM220-AS1 mRNA were as shown. (F) Dual luciferase reporter assays were used to confirm the direct target between TMEM220-AS1 and miR-484. (G) RIP assay was used to detect whether miR-484 could bind with TMEM220-AS1. (H) miR-484 expression in HCC samples and normal samples, from TCGA database. (I) The correlation analysis between miR-484 expression and TMEM220-AS1 expression in HCC samples and normal samples, from TCGA database. (J) miR-484 expression in HCC tumor tissues and adjacent non-tumorous tissues. (K) The correlation analysis between miR-484 expression and TMEM220-AS1 expression in HCC tumor tissues and adjacent non-tumorous tissues, from our dataset. Data were presented as represent the mean ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.