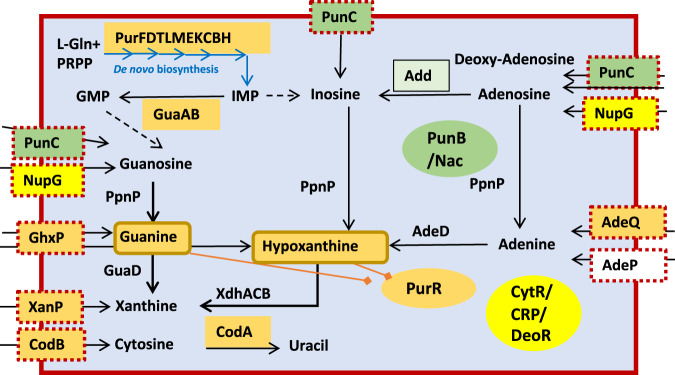
Fig. 1. Metabolic pathways and transcriptional regulons for purine biosynthesis and purine/pyrimidine uptake and salvage genes in E. coli.
The de novo purine biosynthesis pathway is illustrated with blue arrows. Other enzymes involved in purine and pyrimidine metabolism are shown with black arrows. Nucleoside uptake transporters are shown having dashed boxes. PurR is a transcriptional repressor of most of the purine biosynthesis and salvage genes in response to hypoxanthine and guanine. The PurR-regulated genes are highlighted in orange. The purine uptake transporter NupG is under transcriptional control of CytR, DeoR and CRP (shown in yellow). The purine transporter PunC (YdhC), described in this study, is controlled by the LysR-family activator PunR (YdhB) and Nac, as highlighted in green. Abbreviations: IMP, inosine monophosphate; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; GMP, guanosine monophosphate.