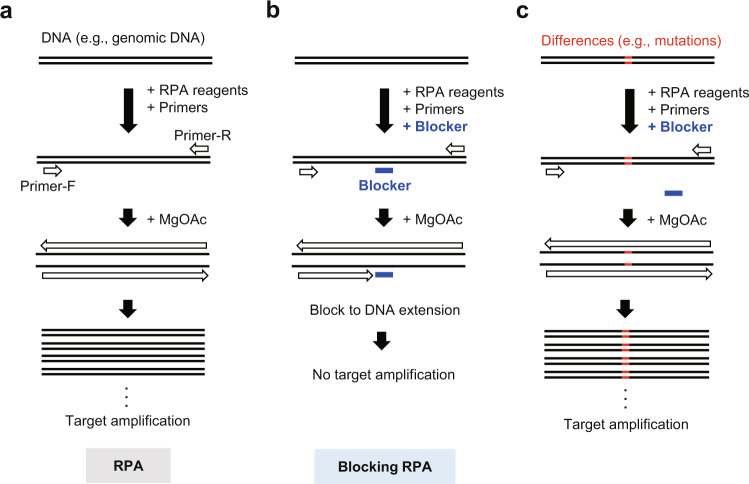
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram showing blocking RPA and its application.
a During RPA, DNA polymerases extend DNA from primers, recruited to their complementary sequences by recombinases, in a magnesium acetate (MgOAc)-dependent manner. b In the presence of a sequence-specific blocker (e.g., ORN), DNA extension by DNA polymerases is inhibited, resulting in the suppression of DNA amplification across the target sequence. c If the target sequence is mutated, it cannot be recognized by the blocking agent, and DNA amplification proceeds uninhibited (allowing for the detection of a DNA mutation).