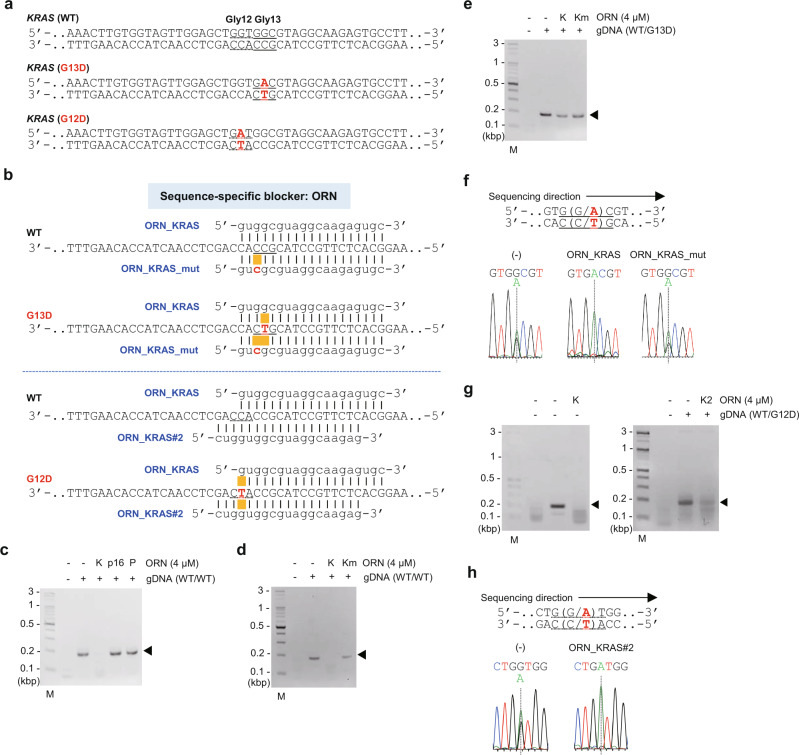
Fig. 2. Blocking RPA using ORNs as blocking agents.
a The WT and mutated sequences of the human KRAS gene. b ORNs examined as sequence-specific blocking agents and their complementary sequence in the human KRAS gene. c, d Results of RPA blocked by an ORN (ORNi-RPA) using template gDNA extracted from 293T cells, which are WT for KRAS. ORNs targeting human KRAS (ORN_KRAS; K), human CDKN2A (p16) (ORN_p16; p16), chicken Pax5 (ORN_cPax5_Ex1B; P), and an ORN that differs from ORN_KRAS by one nucleotide (ORN_KRAS_mut; Km) were used. Amplified KRAS is indicated by an arrowhead. M, molecular weight marker. e Results of ORNi-RPA of gDNA extracted from HCT116 cells, which have both a WT and mutant (G13D) allele of KRAS. f DNA sequencing analysis of ORNi-RPA products. RPA and ORNi-RPA products in e were purified and sequenced using a forward primer. g Results of ORNi-RPA of gDNA possessing both a WT and mutant (G12D) allele of KRAS. h DNA sequencing analysis of ORNi-RPA products. RPA and ORNi-RPA products in g were purified and sequenced using a forward primer.