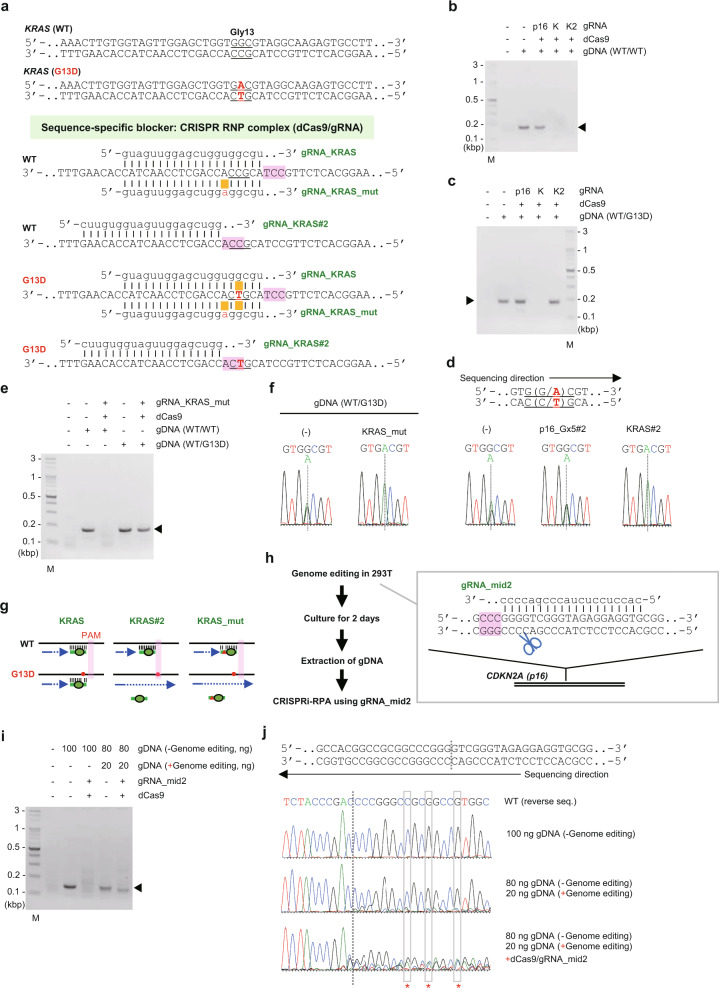
Fig. 3. Blocking RPA using CRISPRi as a blocking agent.
a gRNAs and their target sequences in the human KRAS gene. b, c, e Results of CRISPR interference-RPA (CRISPRi-RPA) of gDNA extracted from 293T (b, e) or HCT116 cells (c, e). A schematic diagram of CRISPRi-RPA is shown in Fig. 1b and Supplementary Fig. 3a. Amplified KRAS is indicated by an arrowhead. M, molecular weight marker. d, f DNA sequencing analysis of CRISPRi-RPA products. CRISPRi-RPA products from c and e were purified and sequenced using a forward primer. g Mechanisms by which the discrimination of a single-nucleotide difference is achieved by CRISPRi-RPA. h A schematic diagram describing the evaluation of genome editing events by CRISPRi-RPA. i Results of CRISPRi-RPA. j Results of DNA sequencing analysis. RPA and CRISPRi-RPA products from i were purified and sequenced using a reverse primer. The CRISPR cleavage site is indicated by vertical dotted lines. The positions where intact CDKN2A (p16) nucleotides were not detected in the CRISPRi-RPA product are marked with asterisks.