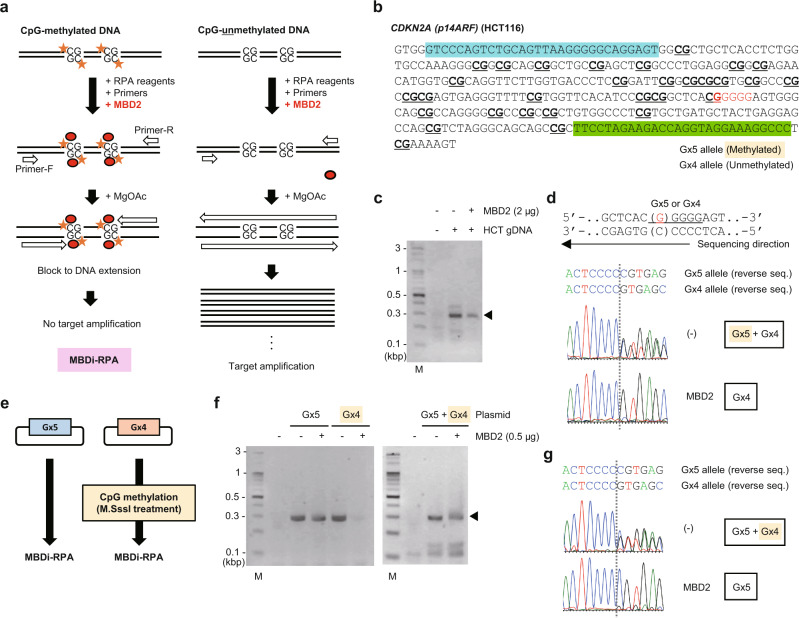
Fig. 4. Blocking RPA to discriminate CpG-methylation status.
a A schematic diagram describing blocking RPA with MBD2 protein as a blocking agent (MBDi-RPA). MBD proteins bind to any methylated CpG sites in a target sequence, resulting in the suppression of amplification. MBDi-RPA can be used to discriminate CpG methylation status. b A target sequence in the human CDKN2A (p14ARF) gene in HCT116. Forward and reverse primer positions are highlighted in blue and green, respectively. c Results of MBDi-RPA. M, molecular weight marker. Amplified CDKN2A (p14ARF) is indicated by an arrowhead. d Results of DNA sequencing analysis. RPA or MBDi-RPA amplicons from c were sequenced using a reverse primer. e A schematic diagram describing MBDi-RPA of in vitro CpG-methylated plasmid DNA. The CDKN2A (p14ARF) sequences shown in b were cloned into plasmid vectors. The sequence corresponding to the Gx4 allele was subsequently methylated in vitro. f Results of MBDi-RPA from individual Gx4 and Gx5 plasmids or a plasmid mixture. g Results of DNA sequencing analysis. RPA and MBDi-RPA amplicons shown in f (plasmid mixture) were sequenced using a reverse primer.