Figure 9.
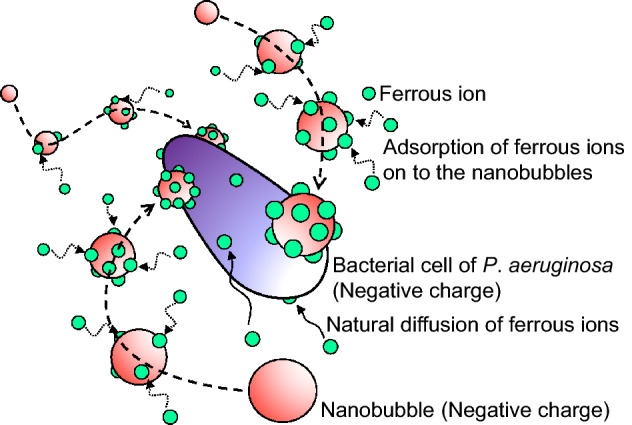
Schematic image of mechanism of ferrous ions delivery to microbial cells by the carbon dioxide nanobubbles. Because the carbon dioxide nanobubbles (red spheres) are negatively charged, cations including ferrous ions (green spheres) are adsorbed on to the surface of the carbon dioxide nanobubbles and change to positive charges. Because bacterial cells (purple rod) are also negatively charged, the carbon dioxide nanobubbles on which ferrous ions are adsorbed are accessible to the bacterial cells and ferrous ions are delivered to the bacteria. Ferrous ions are also delivered to bacterial cells due to natural diffusion, however, the number of ferrous ions delivered to bacterial cells by the carbon dioxide nanobubbles is larger than that delivered due to natural diffusion.
