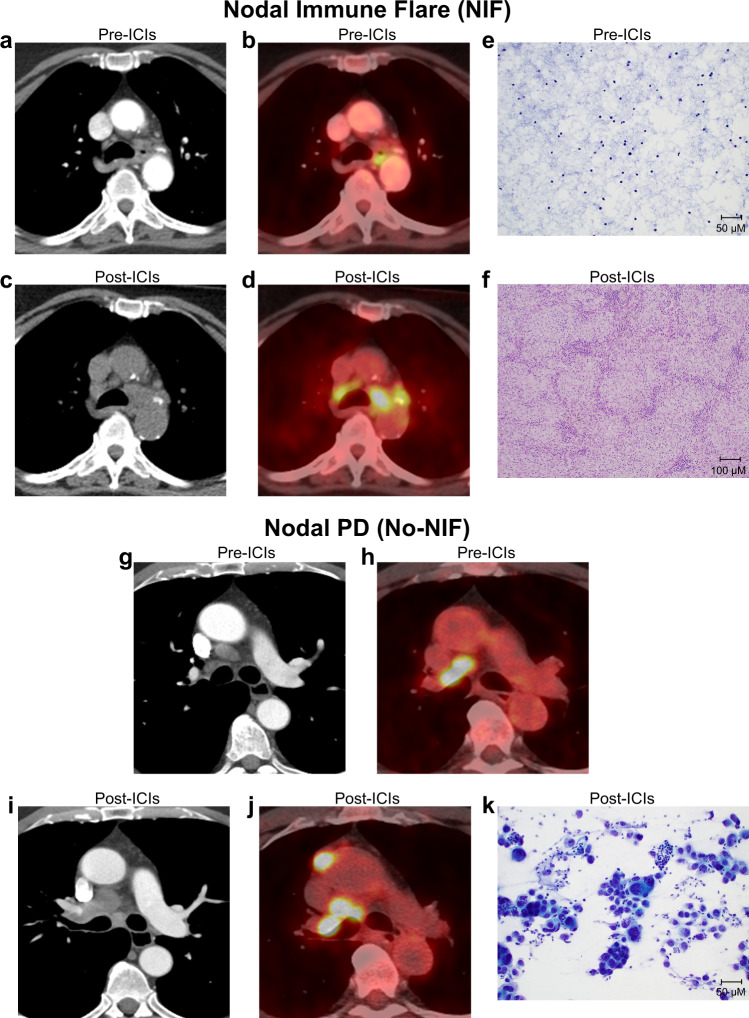
Fig. 1. Radiological and histopathological features of abnormal nodes following neoadjuvant ICIs.
a–d Axial contrast enhanced CT (a), and 18F-FDG PET/CT (b) images of the mediastinum showing normal nodes prior to neoadjuvant treatment with ICIs on NEOSTAR study in a patient with NSCLC (metastasis to station 7; stations 4 R, 4 L, and 11 L negative after invasive baseline mediastinal staging with EBUS). 18F-FDG uptake in the mediastinum is due to esophagitis. Restaging axial CT (c) and 18F-FDG PET/CT (d) images post-neoadjuvant ICIs show marked increase in nodal size and FDG uptake at bilateral mediastinal regions, suspicious for nodal progression. Mediastinoscopy post-neoadjuvant ICIs did not demonstrate carcinoma in lower paratracheal stations (4 L and 4 R). e, f FNA image of paratracheal nodal station pre-therapy (e) demonstrating lack of tumor cells and normal composition (Papanicolaou, x20), and resected station 4 R lymph node post-therapy (f) revealing absence of cancer and evidence of necrotizing non-caseating granulomatous inflammation (hematoxylin and eosin, x10). g–j Axial contrast enhanced CT (g), and 18F-FDG PET/CT (h) images of the mediastinum show nodal enlargement and abnormal 18F-FDG uptake in the right hilum and right mediastinum prior to neoadjuvant ICIs on NEOSTAR study in a patient with NSCLC (baseline invasive mediastinal staging with mediastinoscopy revealed metastasis to station 4 R). Restaging axial contrast enhanced CT (i) and 18F-FDG PET/CT (j) images show increase in size and increase in FDG uptake at right hilar, right mediastinal (4 R) and prevascular nodes, consistent with progression of nodal metastasis. Abnormal nodes were also present at mediastinal 1 R, 2 R and 7 stations post-therapy, which were previously normal at baseline. Subsequent biopsy confirmed carcinoma in the right paratracheal (2 R and 4 R) and subcarinal stations. k FNA image of post-ICI abnormal node (station 7 pictured) revealed the presence of malignancy with disease progression (Papanicolaou, x20). Analyses related to the presented images and micrographs were conducted once. NIF, nodal immune flare; CT, computed tomography; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; FNA, fine needle aspiration; PET, positron emission tomography; PD, progressive disease.