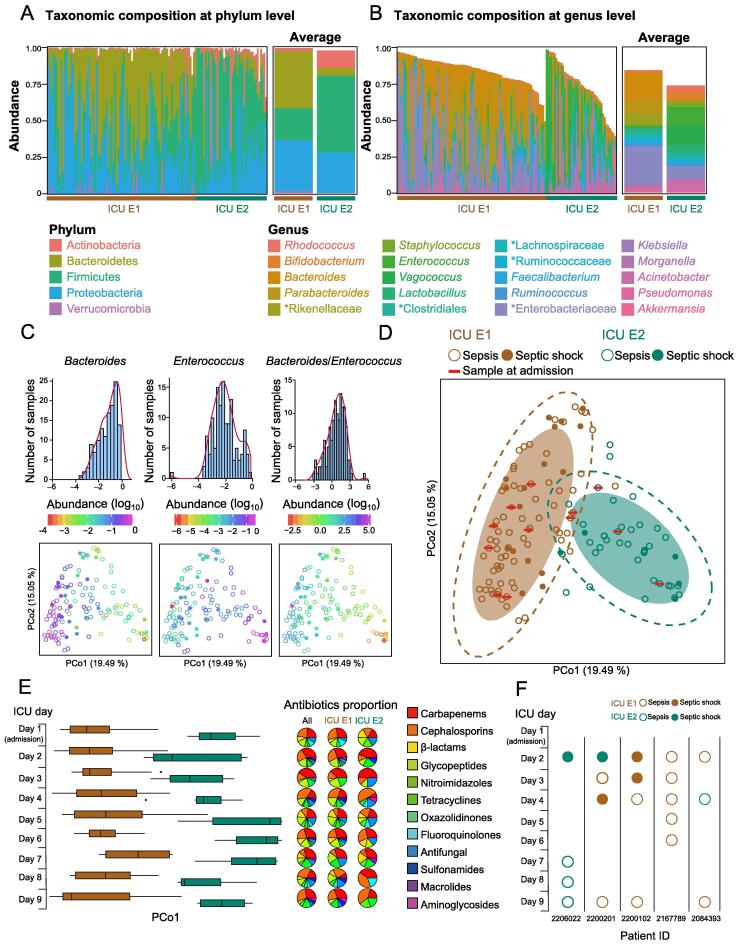
Figure 1.
Two ICU-enterotypes identified in ICU patients with sepsisorseptic shock
Taxonomic composition of 131 fecal samples at the phylum (A) and genus (B) levels. Taxa with relative abundances > 1% among all samples are plotted. Unclassified genera are designated as a higher rank marked by asterisks. The left panel represents the taxonomic composition of each sample; the right panel represents the taxonomic composition of the two ICU-enterotypes using the mean abundance calculated from the data in the left panel. Brown and green bars represent the ICU-enterotypes to which these samples belong. C. Distributions of the log-transformed (log10) relative abundances of the most significantly differing genera. The top panel displays the observed distributions using a frequency distribution histogram with density curve. The bottom panel displays these distributions in ICU-enterotype space represented by JSD-based PCoA plot. Solid circles represent samples from septic shock patients; hollow circles represent samples from septic patients. Colored PCoA plot: log-transformed (log10) relative abundances of the genera for each sample. D. Gut microbiota compositions of individual patients with ICU E1 (n = 89) and ICU E2 (n = 42) are plotted on a JSD-based PCoA plot at the genus level. Shaded ellipses represent the 80% CI; dotted ellipses represent the 95% CI. E. In the left panel, the daily fecal sample distributions are plotted against the PCo1 axis (D). Boxes represent the IQR between the first and third quartiles; the line inside represents the median. Whiskers denote the lowest and highest values within 1.5× IQR from the first and third quartiles, respectively. In the right panel, the proportions of antibiotics used on each day are displayed using all samples, ICU E1 samples, and ICU E2 samples, respectively. F. Variation in ICU-enterotypes from five patients (IDs shown at the bottom) along the 9-day observation. Figure S1 shows all patients’ results. JSD-based PCoA, Jensen-Shannon distance-based principal coordinate analysis; ICU E1, ICU-enterotype I; ICU E2, ICU-enterotype II; CI, confidence interval; IQR, interquartile range.