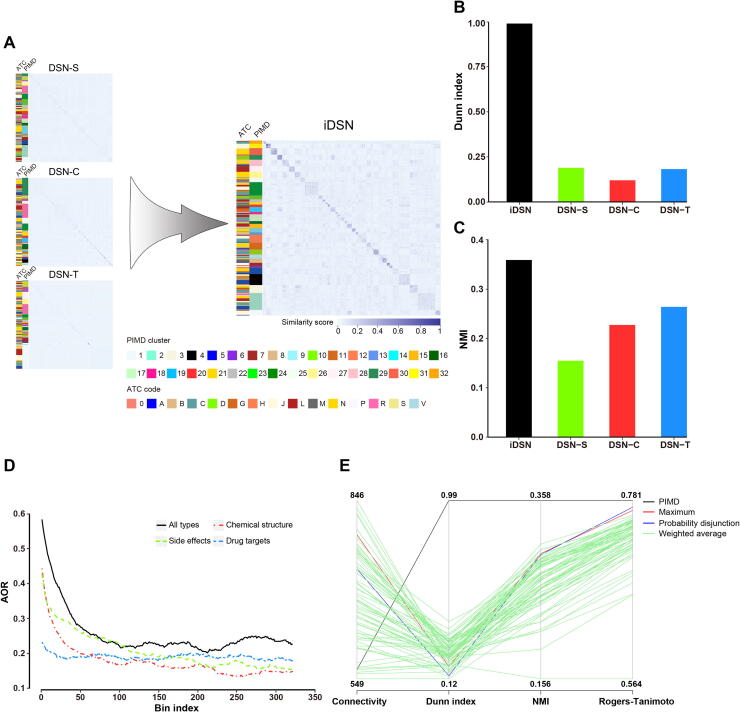
Figure 3.
Performance of the iDSN
A. Heatmaps of DSNs. DSN-S, DSN-C, and DSN-T were integrated into the iDSN. The two sidebars to the left of the networks correspond to the original ATC code (left) and PMID cluster label (right) separately. B. Dunn index for DSN-S, DSN-C, DSN-T, and iDSN. C. NMI for DSN-S, DSN-C, DSN-T, and iDSN. D. AOR for DSN-S, DSN-C, DSN-T, and iDSN. A bin composed of 3000 drug pairs was slid from the top to the bottom of the drug pair list with a step size of 100. AOR was calculated for each bin and that for the first 320 bins is plooted here. E. PIMD outperforms other integrative methods for DSN clustering. For the weighted average method, multiple drug similarity matrices were averaged by traversing weight. The weight of each DSN ranges from 0 to 1 with the step of 0.1. NMI, normalized mutual information; AOR, ATC overlap rate.