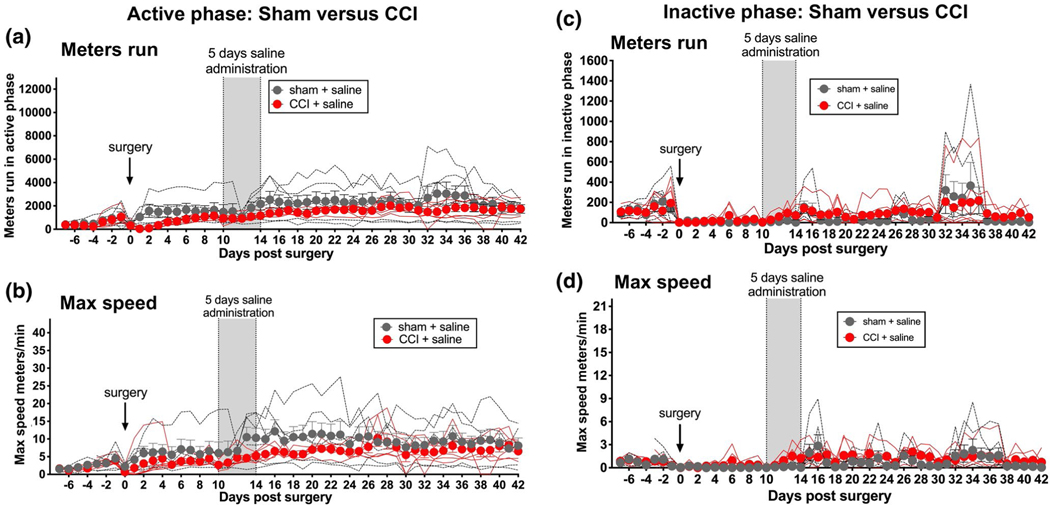
FIGURE 1.
Enduring reduction of active (dark) phase voluntary wheel running by sciatic nerve injury. Unilateral sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury (CCI), which induces prolonged and stable neuropathic pain, induced prolonged and stable suppression of voluntary wheel running distance (a) and maximal running speed (b), relative to sham controls in the active phase. Five days of twice daily systemic saline (vertical gray bar) was administered beginning on Day 10 after surgery so to provide a regimen comparable to that followed in subsequent experiments. No such changes were observed in these same rats in the light phase (c, d). n = 5–6 per group