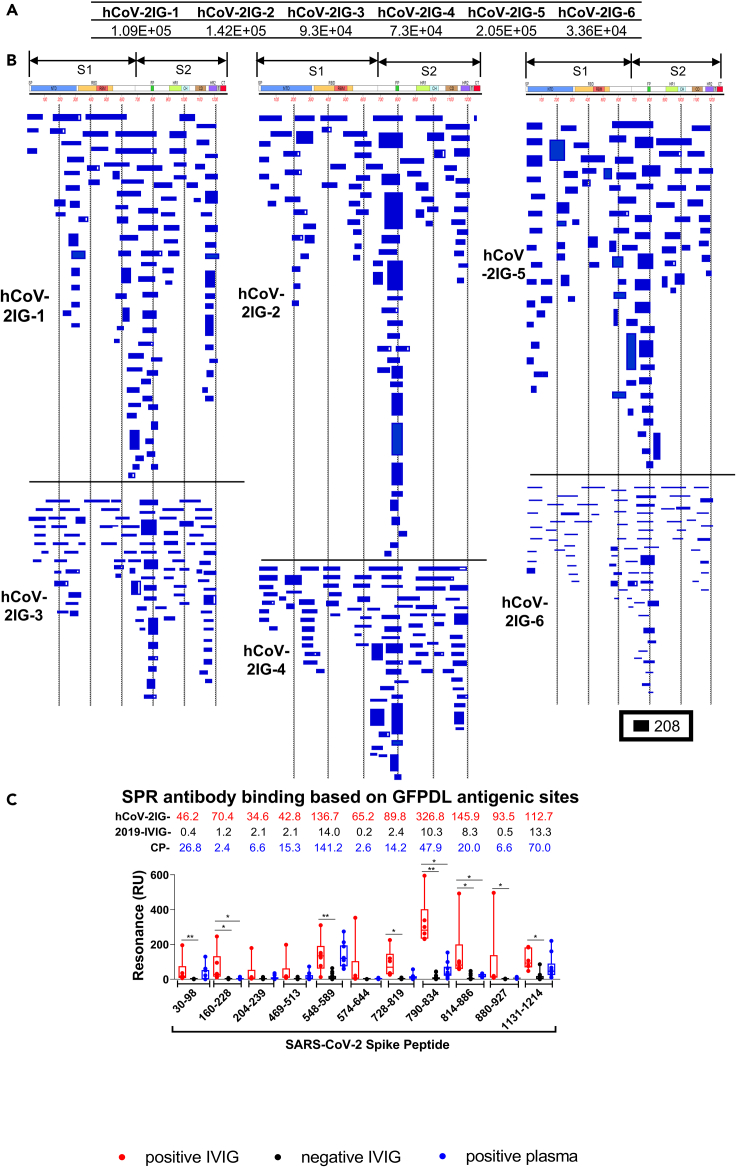
Figure 1.
SARS-CoV-2 spike antibody epitope repertoires recognized by hCoV-2IG
SARS-CoV-2 spike GFPDL analyses of IgG antibodies in six batches of hCoV-2IG.
(A) Number of IgG bound phage clones selected using SARS-CoV-2 spike GFPDL for each of the six individual lots of hCoV-2IG (hCoV-2IG-1 to hCoV-2IG-6).
(B) Epitope repertoires of IgG antibody in hCoV-2IG batches and their alignment to the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Graphical distribution of representative clones with a frequency of >2, obtained after affinity selection, are shown. The horizontal position and the length of the bars indicate the alignment of peptide sequence displayed on the selected phage clone to its homologous sequence in the SARS-CoV-2 spike. The thickness of each bar represents the frequency of repetitively isolated phage. Scale value is shown enclosed in a black box beneath the alignments. The GFPDL affinity selection data was performed in duplicate (two independent experiments by researcher in the lab, who was blinded to sample identity), and a similar number of phage clones and epitope repertoire was observed in both phage display analysis.
(C) SPR binding of hCOV-2IG (n = 6; in red), control pre-pandemic 2019-IVIG (n = 16; in black) and convalescent plasma (n = 9; in blue) with SARS-CoV-2 spike antigenic site peptides identified using GFPDL analysis in Figure 1B. The amino acid designation is based on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein sequence (Figure S1). Total antibody binding is represented in maximum resonance units (RU) in this figure for 10-fold serum dilution of CP, and 1mg/mL of 2019-IVIG or hCoV-2IG. The numbers above the peptides show the mean value for each respective group antibody binding to the peptide and is color-coded (6 hCOV-2IG in red, 16 2019-IVIG in black, and 9 CPs in blue). All SPR experiments were performed twice and the researchers performing the assay were blinded to sample identity. The variations for duplicate runs of SPR was <4%. The data shown are average values of two experimental runs. The statistical significances between the hCoV-2IG vs 2019-IVIG vs CP for antibody binding to each peptide were performed using multiple group comparisons by non-parametric (Kruskal-Wallis) statistical test using Dunn's post-hoc analysis in GraphPad prism. The differences were considered statistically significant with a 95% confidence interval when the p value was less than 0.05. (∗, p values of ≤0.05, ∗∗, p values of ≤0.01).