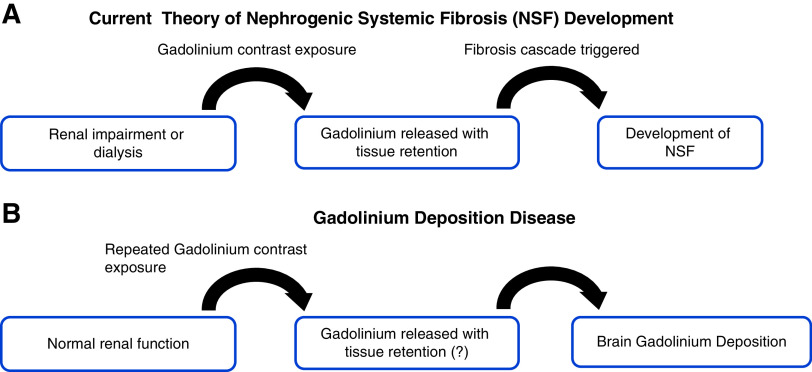
Figure 1.
Gadolinium exposure implicated in the development of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF) and Gadolinium Deposition Disease. (A) Current prevailing pathogenesis theory of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Patients with renal impairment or on dialysis are exposed to gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA) with retention of these agents due to low renal function. Gadolinium is liberated with decreased clearance leading to tissue deposition and ultimately triggering fibrosis resulting in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. (B) Gadolinium deposition disease pathogenesis theory is less clear. Most notable are recurrent exposures to GBCA in those with normal renal function and its association with brain deposition of gadolinium, but the mechanism is unclear. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.