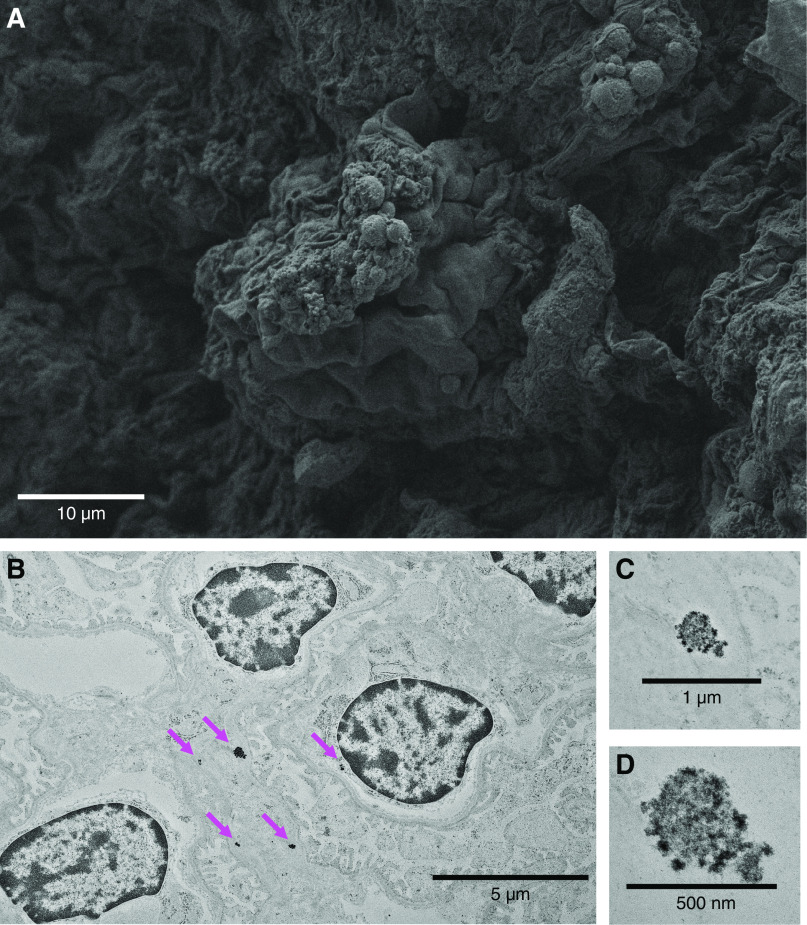
Figure 2.
Gadolinium-based contrast agents induce renal glomerular changes. It has been demonstrated that gadolinium-based contrast agent treatment induces hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, and the Warburg effect in renal cortex (33). (A) Renal cortex from contrast-treated animals demonstrated lipid-like droplets. Scanning electron microscopy in fixed renal cortical sections (Zeiss Sigma 300 field emission scanning electron microscopy of formalin/glutaraldehyde-fixed tissue, osmicated—1 for 1 hour). (B) Electron densities in the glomeruli of contrast-treated mice. High electron densities (magenta arrows) occurred intracellularly and in the subepithelial basement membrane. (C and D) High-magnification imaging demonstrates that these nanostructures have a spiculated, sea urchin–like appearance previously reported in skin (20). Transmission electron microscopy, Hitachi HT7700 with AMT 16-megapixel digital camera. Herein, fixed sections of 80-nm thickness were stained with osmium for the transmission electron microscopy images obtained with the Hitachi HT7700.