Fig. 1. IPNS catalysis is amenable to tr-SFX analysis.
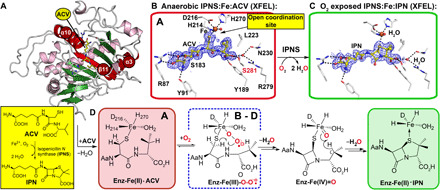
(A) Protein fold of anaerobic IPNS:Fe(II):ACV (conformation A, PDB: 1BLZ) (26); Fe, orange sphere; ACV, yellow; α-helices, purple; β strands, green; except elements involved in ACV binding/flexible regions due to O2 binding; red. (B) Composite SFX 2mFo-DFc omit electron density map for anaerobic IPNS:Fe:ACV (PDB: 6ZAE, 1.0 σ contour level, 1.40-Å resolution; fig. S2), showing key ACV interactions (R87, Y91, S183, Y189, L223, N230, R279, and S281) highlighting S281 (red), which is important in dynamics. (C) Composite SFX 2mFo-DFc omit map for IPNS:Fe:IPN obtained by ~30-min O2 exposure of IPNS:Fe:ACV microcrystals (PDB: 6ZAQ, 1.0 σ contour level, 1.60-Å resolution; fig. S2). (D) Key intermediates with the superoxide (ACV conformations B to D, further addressed in Fig. 3 due to ACV rearrangement after O2 binding) in a blue dashed box. Note: The exact localization of the electrons in the Fe superoxo complex is unknown. To reflect this, we have used the nomenclature Fe-O2⸣●−.
