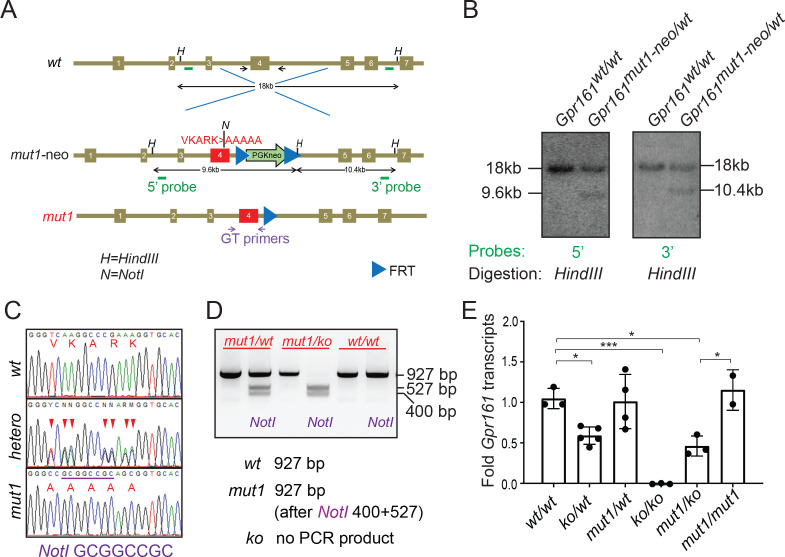
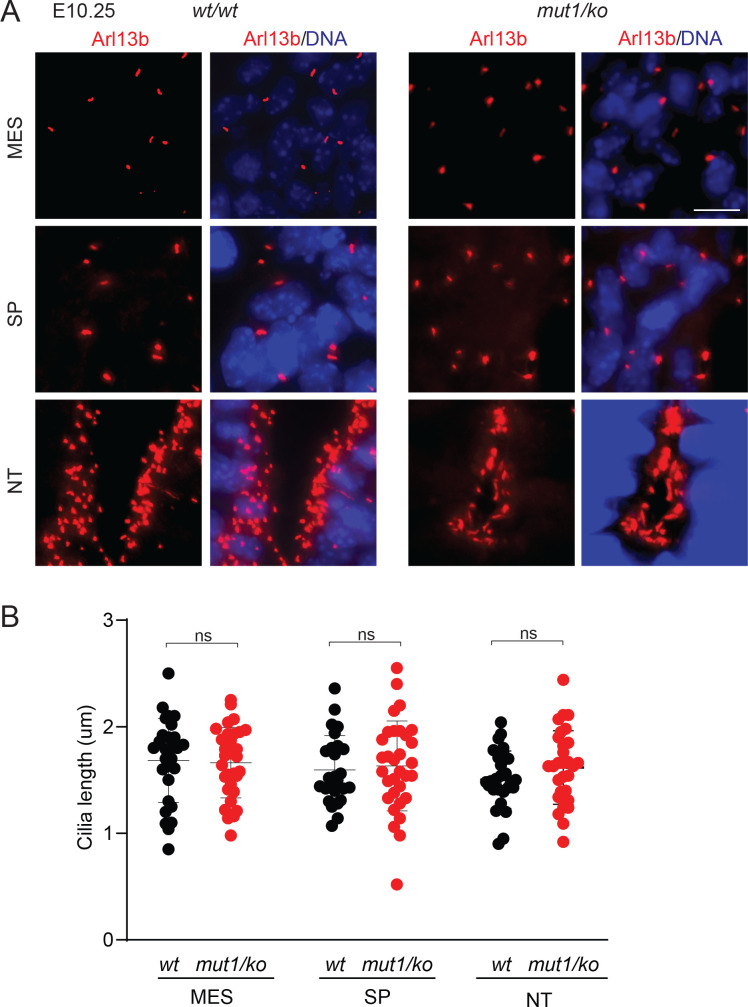
Figure 2. Generating ciliary localization defective endogenous knock-in Gpr161mut1 mouse model.
(A) The gene targeting strategy used to engineer the Gpr161mut1 allele. Exons are numbered based on NM_001081126.2. PGKneo and FRT cassettes and genotyping (GT) primer sequences are indicated. The mut1 sequence is located on Exon 4. (B) Southern blot analysis of representative ES cell clones using the 5’ and 3’ probes in A. (C) Sanger sequencing of Gpr161wt and Gpr161mut1 alleles in adult mouse-tail DNA. Double peaks in Gpr161wt/mut1 heterozygote indicated by arrowheads. The engineered NotI restriction site (GCGGCCGC) is indicated by a purple bar. (D) Genotyping for wild type, Gpr161mut1 and knockout (ko) alleles by PCR using designated primers shown in A and digesting with NotI. (E) qRT-PCR of Gpr161 transcripts normalized to Hprt in whole embryo extracts at E9.5 indicate diminished mRNA expression in the Gpr161 knockout (ko/ko) embryos compared to wild type (wt/wt), but unchanged in mut1/mut1 embryos. Data shown as mean ± SD. n=3 (wt/wt), 5 (ko/wt), 4 (mut1/wt), 3 (ko/ko), 3 (ko/mut1), 2 (mut1/mut1) embryos. *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001. Other pairwise comparisons are not significantly different.
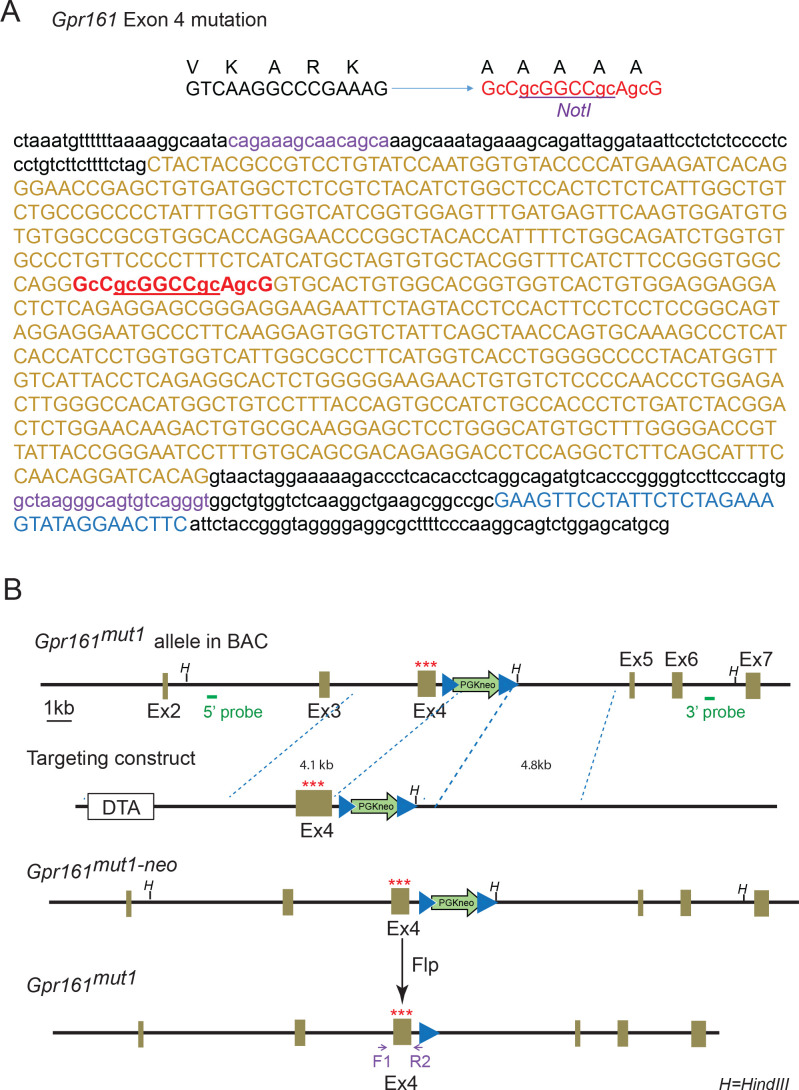
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Genomic DNA sequence and scheme of Gpr161mut1 allele.
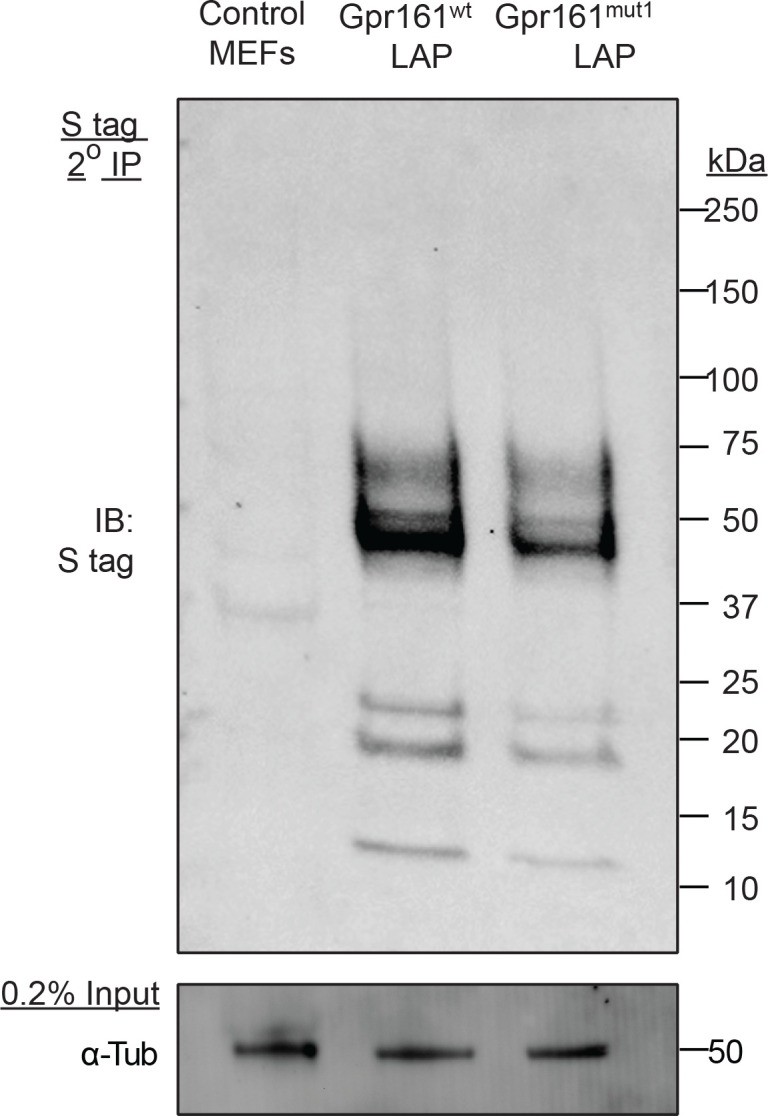
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Tandem affinity purification of LAP-tagged Gpr161wt or Gpr161mut1 (see Materials and methods) stably expressed in wild type MEFs was followed by immunoblotting for S-tag.