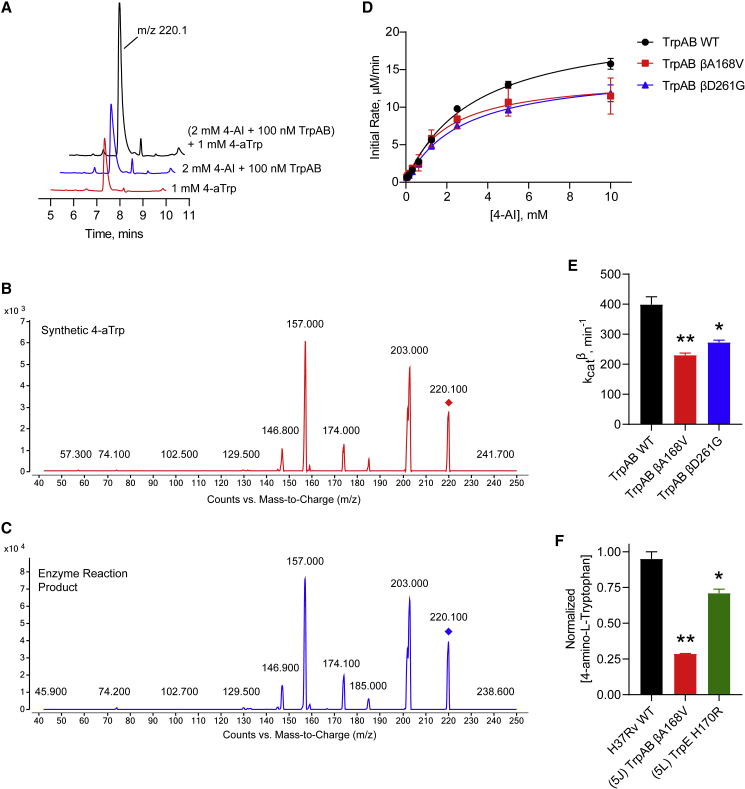
Figure 6.
TrpB converts 4-AI to 4-amino-L-Trp in vitro and in Mtb
(A) Representative chromatograms of synthetic 4-aTrp (red trace), the enzymatic reaction mixture obtained by incubating TrpAB with 4-AI (blue trace), and the enzyme reaction spiked with synthetic 4-aTrp (black trace).
(B and C) Fragmentation pattern of synthetic 4-aTrp (B) and the enzyme reaction mixture (C) in a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
(D) 4-AI was incubated with WT or mutant TrpAB in the presence of saturating L-Ser concentrations. The resulting 4-aTrp was quantified using LC-MS. Data shown are mean ± SEM (n = 2).
(E) Calculated catalytic efficiency, kcat, of the WT and mutant TrpAB in (D). Bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 2). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 when compared with the WT kcat using one-way ANOVA.
(F) Intracellular 4-AI incorporation into 4-aTrp was measured by extracting the metabolites using 1:1 ACN:MeOH. The concentration of 4-aTrp produced within the indicated C1R mutants were normalized against that of the WT. Bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 2). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 when compared with the WT using one-way ANOVA.