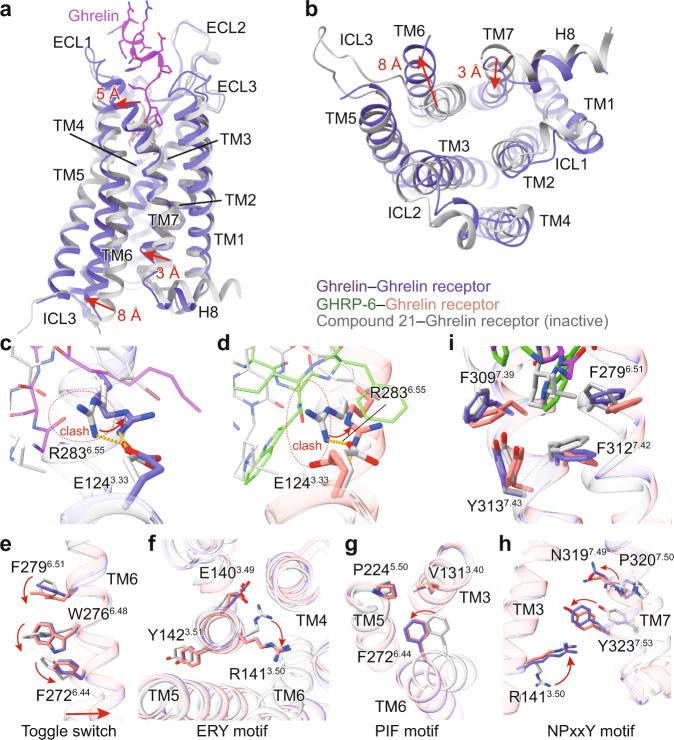
Fig. 4. Activation mechanism of ghrelin receptor.
a, b Structural superposition of the active and antagonist-bound ghrelin receptor. (a) side view; (b) cytoplasmic view. c, d Conformational changes of the salt bridge comprising of E1243.33 and R2836.55 upon peptide activation. Ghrelin and GHRP-6 push the side-chain of R2836.55 to swing away from the receptor helical core due to steric clash. The swing orientations of E1243.33 and R2836.55 were indicated by red arrows. The clashes were highlighted as red oval dashed lines. e-h Conformational changes of the conserved “micro-switches” upon receptor activation. (e) Toggle switch, (f) ERY motif, (g) PIF motif, (h) NPxxY motif. The outward displacement of TM6 of the active receptor is shown as a red arrow (e). The conformational changes of residue side chains are shown as red arrows upon receptor activation. i The hydrophobic cluster comprising F2796.51, F3097.39, F3127.42, and Y3137.43 stabilizes the inter-helical hydrophobic contacts between TM6 and TM7. Ghrelin is shown in magenta, ghrelin-bound ghrelin receptor in slate blue. GHRP-6 is displayed in green, and GHRP-6 bound ghrelin receptor in salmon. The compound 21-bound ghrelin receptor (PDB: 6KO5), is colored in gray.