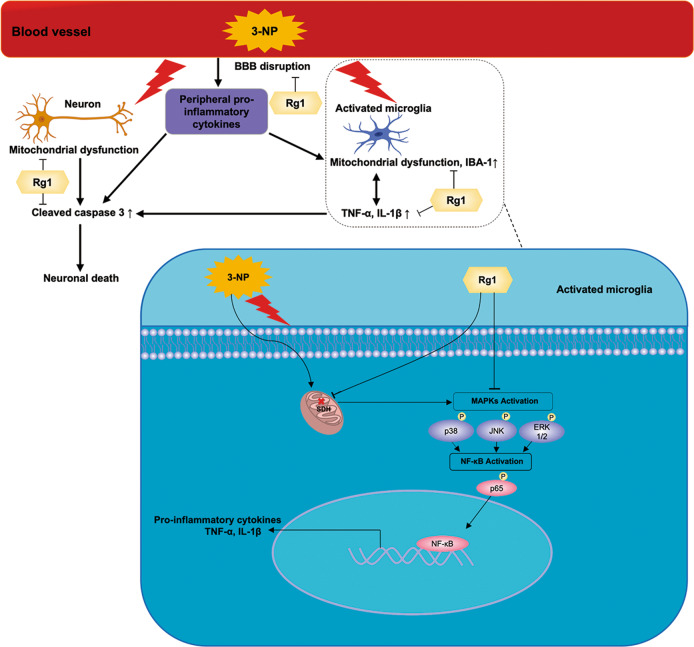
Fig. 9. The schematic diagram for possible mechanisms of Rg1’s neuroprotective effects in 3-NP induced HD mouse model.
3-NP inhibits the activity of SDH in striatal cells, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and the death of neurons in the striatum, and it also induces BBB disruption, which leads to the leakage of more peripheral proinflammatory cells and microglia into the CNS. In microglia, 3-NP induces the activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Rg1 alleviates 3-NP-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and BBB breakdown, and it also contributes to the survival of striatal neurons by inhibiting striatal microglial activation, apoptosis, and the expression of proinflammatory cytokines induced by 3-NP. Moreover, Rg1 protects against striatal neuronal death by suppressing the activation of proteins in the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.