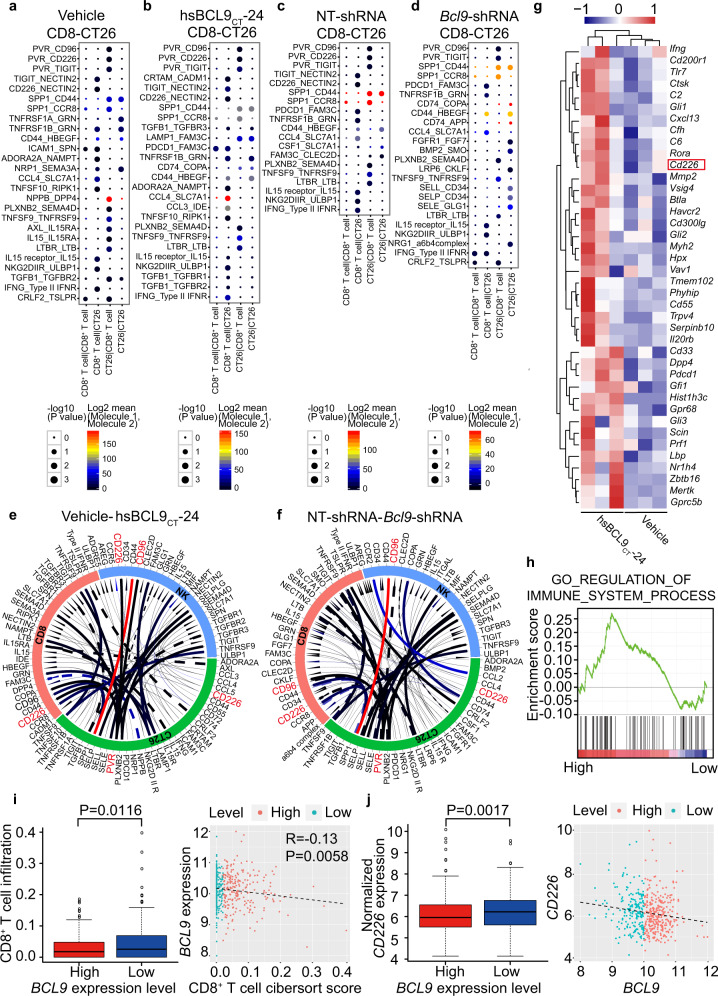
Fig. 4.
BCL9 is associated with CD155-CD226 checkpoint in CT26-CD8 T+ cell interaction. a Interaction analysis between CD8+ T and CT26 cells in vehicle group. b Interaction analysis between CD8+ T and CT26 cells in hsBCL9CT-24 treated group. c Interaction analysis between CD8+ T and CT26 cells in NT-shRNA group. d Interaction analysis between CD8+ T and CT26 cells in Bcl9-shRNA group. e Circos plots of all of the putative ligand–receptor interactions in vehicle and hsBCL9CT-24 treated groups. The color of the line represents the average expression of the ligand–receptor pair in the pair of cells, and the thickness of the line represents the significance of the ligand–receptor enrichment in the pair of cells. The solid line represents the interaction of the hsbcl9CT-24 group, and the dotted line represents the interaction of the vehicle group. f Circos plots of all of the putative ligand–receptor interactions in NT-shRNA and Bcl9-shRNA groups. The solid line represents the interaction of Bcl9-shRNA group, and the dotted line represents the interaction of the NT-shRNA group. g Heatmap analysis of CT26 tumor pretreated with vehicle or hsBCL9CT-24 (i.p., 25 mg/kg). h GSEA analysis of CT26 tumor pretreated with vehicle or hsBCL9CT-24 (i.p., 25 mg/kg). i Scatter and boxplot analyses of CD8+ T cell infiltration associated with BCL9 expression level in TCGA. j Scatter and boxplot analyses of CD226 expression associated with BCL9 expression level in TCGA. P < 0.05 means statistically significant.