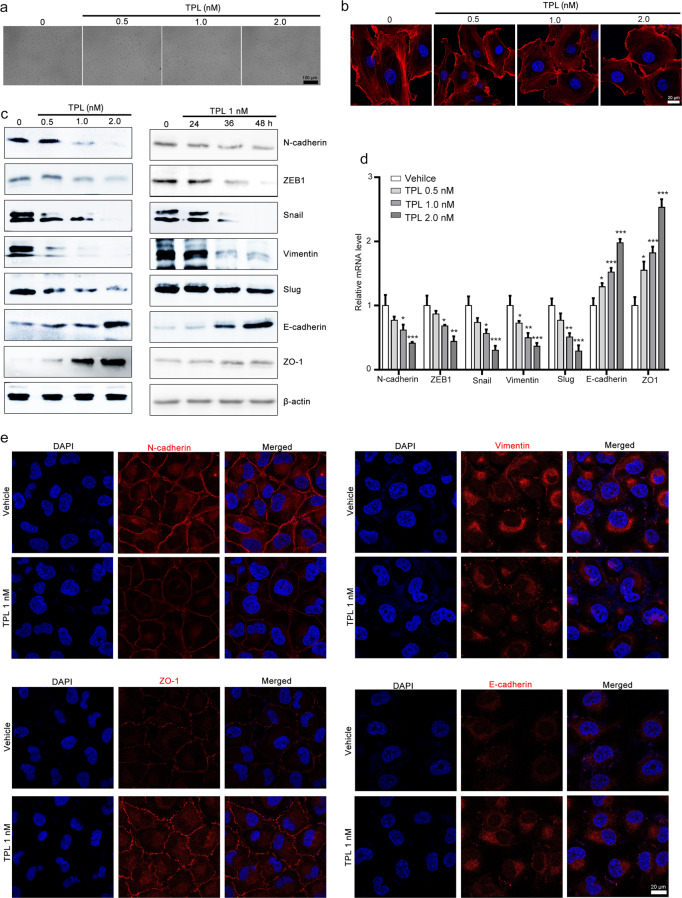
Fig. 2. Triptolide suppresses EMT in NCI-H1299 cells.
The effect of triptolide on the morphology of NCI-H1299 cells. NCI-H1299 cells were exposed to various concentrations of triptolide for 48 h, and morphological changes were observed with a microscope (×100 magnification) (a) and with a laser scanning confocal microscope (×40 magnification) after staining using rhodamine-phalloidin (b). c, d The effect of triptolide on EMT markers in NCI-H1299 cells. The cells were exposed to various concentrations of triptolide for 48 h or 1 nM triptolide for 24, 36, and 48 h. The cells were harvested and subjected to Western blotting and RT-qPCR assays to detect the expression of ZEB1, N-cadherin, vimentin, slug, snail, ZO-1, and E-cadherin. β-Actin and GAPDH were used as internal controls in Western blotting and RT-qPCR assays. The results of Western blotting and RT-qPCR assays are presented in c and d, respectively. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM, n = 3. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 vs. the vehicle group. e Triptolide modulated the expression of EMT markers, as indicated by immunofluorescence staining. NCI-H1299 cells were treated with or without triptolide for 48 h, and then, E-cadherin, ZO-1, vimentin, and ZEB1 expression was detected using an immunofluorescence staining assay. DAPI was used to visualize the nuclei. Images were taken using a Zeiss LSM 800 confocal microscope with a ×63 oil immersion lens. TPL triptolide.