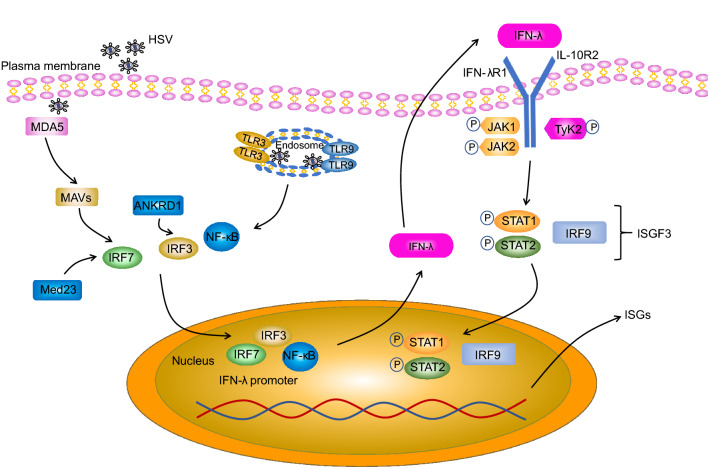
Fig. 1.
Pathway of Type III IFN induction and signaling, and interaction of type III IFN with HSV. HSV molecular patterns are recognized by TLR3 and TLR9 in the endosome and/or MDA5 in the cytoplasm, leading to the activation of the NF-κB, IRF3 and IRF7 transcription factors and their subsequent translocation to the nucleus where they stimulate IFN-λ gene transcription. Med23 and ANKRD1 are direct targets of IRF7 and IRF3 respectively and upregulate type III IFN expression. Secreted IFN-λ binds to a heterodimeric receptor composed of the IFNLR1 and IL-10RB receptor chains. IFN-λ binding leads to activation of JAK1/TYK2, which in turn leads to tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT2, resulting in the formation of STAT1–STAT2 heterodimers. Subsequently, STAT1–STAT2 heterodimers associate with IRF9, forming the ISGF3 complex, which then moves to the nucleus and triggers expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs).