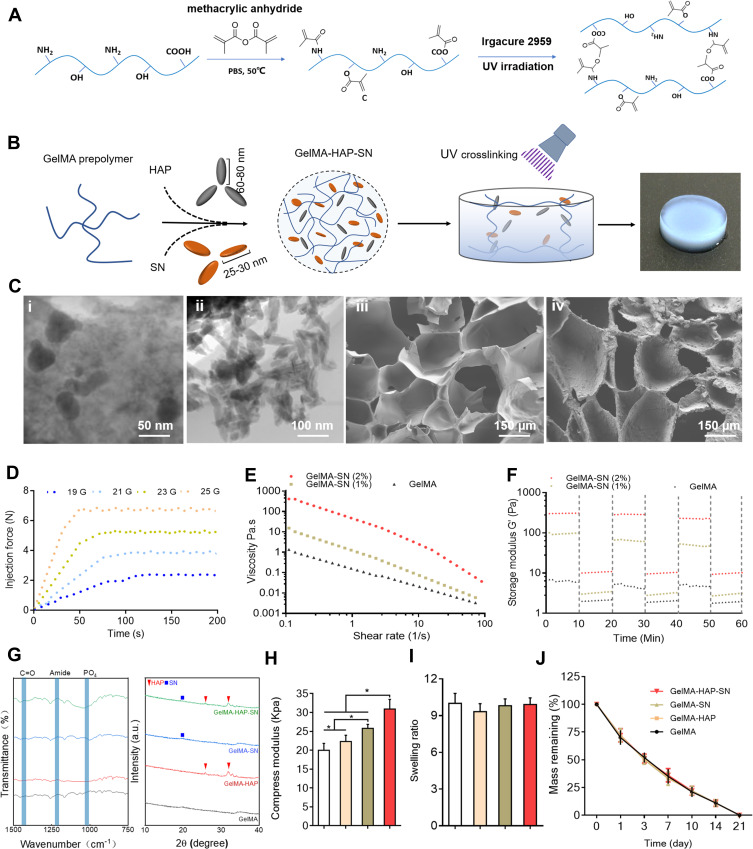
Figure 1.
Fabrication and characterization assay of GelMA-HAP-SN hydrogel. (A) Chemical synthesis of the GelMA from gelatin and methacrylic anhydride and UV cross-linking structure of the GelMA. (B) Fabrication of GelMA-HAP-SN hydrogel. (C) Electron microscopy of the nanoparticles and the hydrogel. i–ii TEM observation of SN and HAP; iii–iv SEM observation of GelMA with and without the nanoparticles. (D) GelMA-HAP-SN hydrogel (uncross-linked) injectability demonstrated using a syringe with various needle sizes at room temperature. (E–F) Viscosity and storage modulus assay of SN-loaded GelMA hydrogel with various SN concentrations. (G) Chemical composition assay of GelMA, GelMA-HAP, GelMA-SN, and GelMA-HAP-SN hydrogel using Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer X-ray diffraction. (H–I) Calculated swelling rate and compression modulus of GelMA-based hydrogel after UV cross-linking. (J) Degradation rate of GelMA, GelMA-HAP, GelMA-SN, and GelMA-HAP-SN hydrogel after UV cross-linking. *P < 0.05 indicates statistical difference.