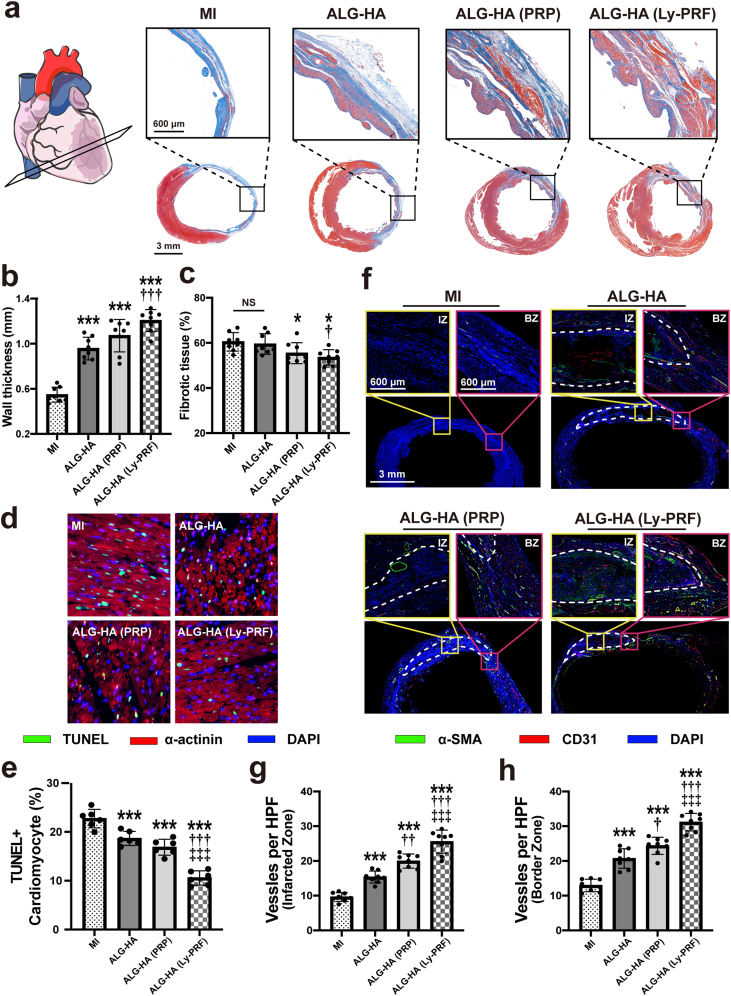
Fig. 4.
The ALG-HA hydrogel with Ly-PRF attenuate LV remodeling, improved angiogenesis and reduces apoptosis of cardiomyocyte. (a) Masson's trichrome staining for all groups at day 28. (b, c) Quantitative analysis of wall thickness (b) and fibrotic tissue (c); n = 8 animals per group. (d, e) Representative images of TUNEL staining (d) and assessment of cardiomyocyte apoptosis in BZ (e) at day 7; n = 8 animals per group. (f) Sections were stained with α-SMA (green), CD31 (red) and DAPI (blue) to visualize the arteries in IZ and BZ at day 28. The white dotted line indicated the edge of the hydrogel. (g, h) The number of arteries was counted in IZ (g) and BZ (h) at day 28; n = 8 animals per group. The data in (b, c, e, g and h) were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. NS indicates not significant. ***p < 0.001 and *p < 0.05 compared with MI group; †††p < 0.001, ††p < 0.01 and †p < 0.05 compared with ALG-HA group; ‡‡‡p < 0.001 compared with ALG-HA (PRP) group. MI, myocardial infarction; ALG, alginate; HA, hyaluronic acid; PRP, platelet rich plasma; Ly-PRF, lyophilized platelet-rich fibrin; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling; IZ, infarcted zone; BZ, border zone. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)