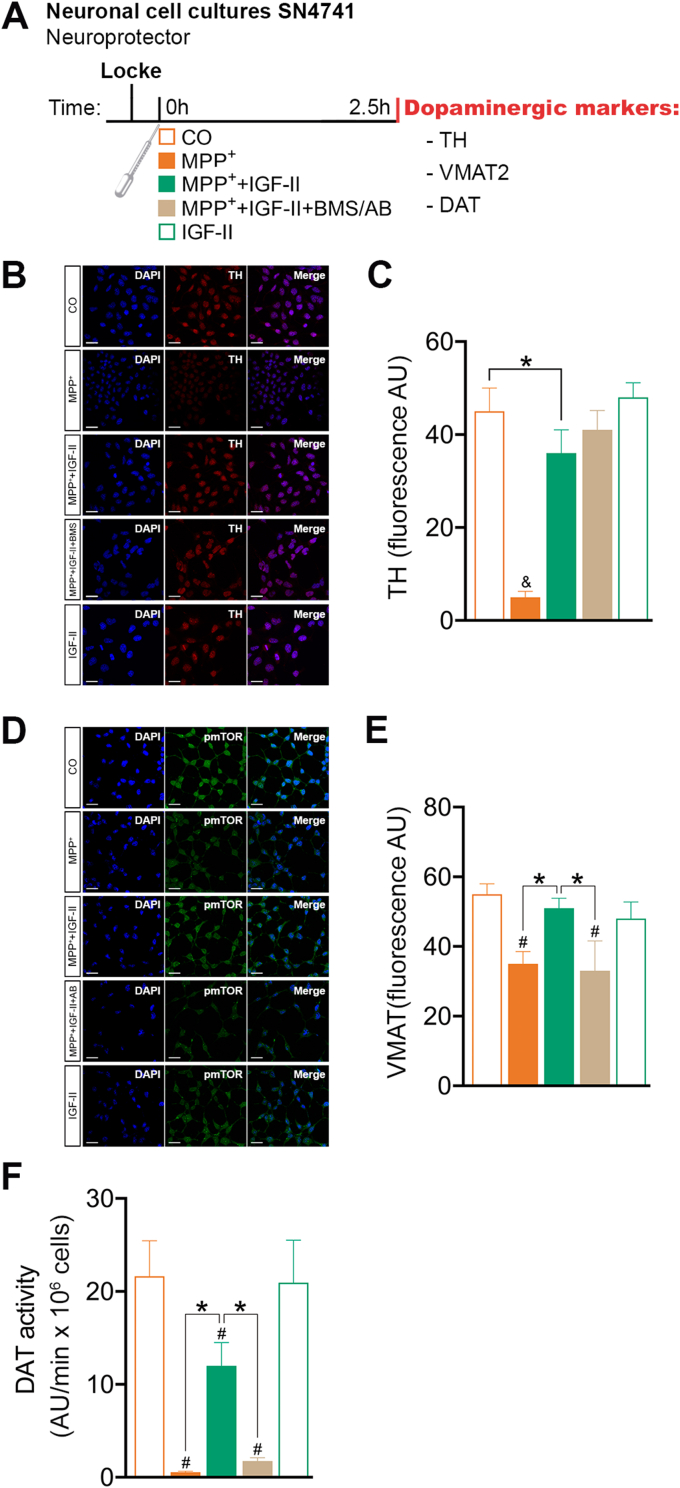
Fig. 4.
IGF-II protects SN4741 dopaminergic cells against MPP+-induced toxicity. (A) Experimental design for the study of the effects of IGF-II on dopaminergic markers. The measures were taken in SN4741 cells after 2.5 h of incubation with MPP+, in the presence or absence of IGF-II and/or BMS and AB. (B) Representative Immunocytochemistry stain for DAPI and TH. (C) Quantification of TH immunofluorescence; BMS is used to define the receptor involved in the IGF-II effect. (D) Representative immunocytochemistry stain for DAPI and VMAT2. (E) Quantification of VMAT2 immunofluorescence; AB is used to define the receptor involved in the IGF-II effect. (F) DAT activity; AB is used to define the receptor involved in the IGF-II effect. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 6 each group (3 independent experiment). #P < 0.05, versus CO and IGF-II groups; *P < 0.05, versus groups connected in bars; & P < 0.05, versus all other groups. Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test.