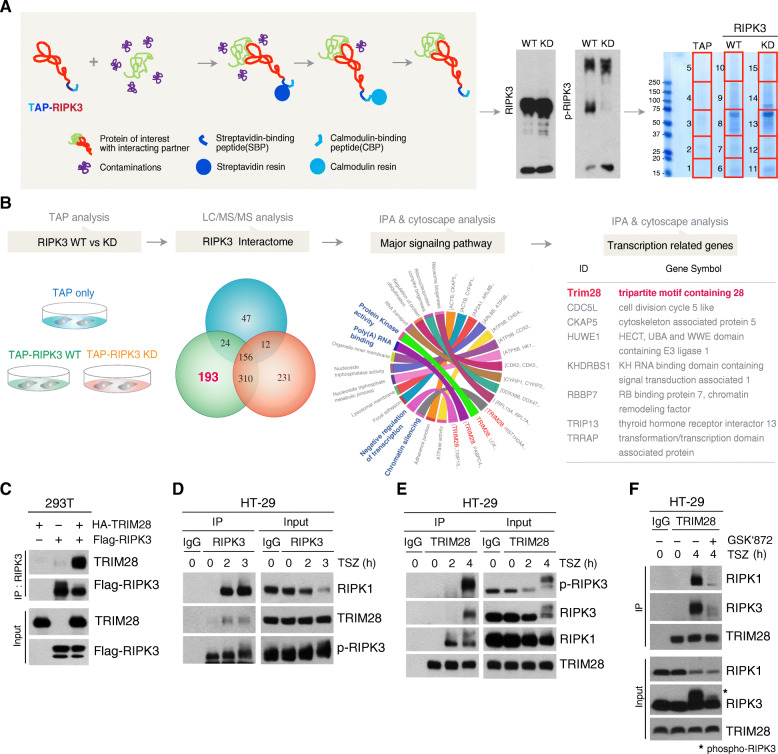
Fig. 2.
TRIM28 is a transcriptional regulator during necroptosis. (A) Schematic of the two step-purification workflows of RIPK3-binding proteins using a tandem affinity purification (TAP) system (left). TAP-mock, TAP-RIPK3 WT, or TAP-RIPK3-KD constructs were transiently transfected into the 293 T cells. Following 18 h of expression, the cells were lysed and subjected to two steps of purification. Validation of RIPK3 activity and its enrichment was performed by immunoblot analysis with RIPK3 or phospho-RIPK3 antibodies (middle). An aliquot of each purified sample was loaded to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. Potential RIPK3-binding proteins were identified by LC-MS/MS. Red square boxes indicate the excised regions of the gels subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis (right). (B) Venn diagram represents the overlap of proteins and unique proteins identified by LC/MS/MS among TAP-purified samples as indicated. Total 193 proteins were identified as specific RIPK3 binding proteins. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) and cytoscape with cluego plug-in were used for bioinformatic analysis of 193 RIPK3 binding proteins and the enriched GO term/KEGG pathway are illustrated using a chord diagram. Finally, we identified eight potential RIPK3-binding proteins linked to transcriptional regulation. (C) 293 T cells were transfected with Flag-RIPK3 in the absence or presence of HA-TRIM28. After 24 h, cells were harvested and immunoprecipitated with RIPK3 antibodies. (D and E) HT-29 cells were treated with TSZ for the indicated times, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with RIPK3 (D) or TRIM28 antibodies (E). (F) HT-29 cells were pretreated with GSK’872 for 1 h and with TSZ for 4 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with TRIM28 antibodies