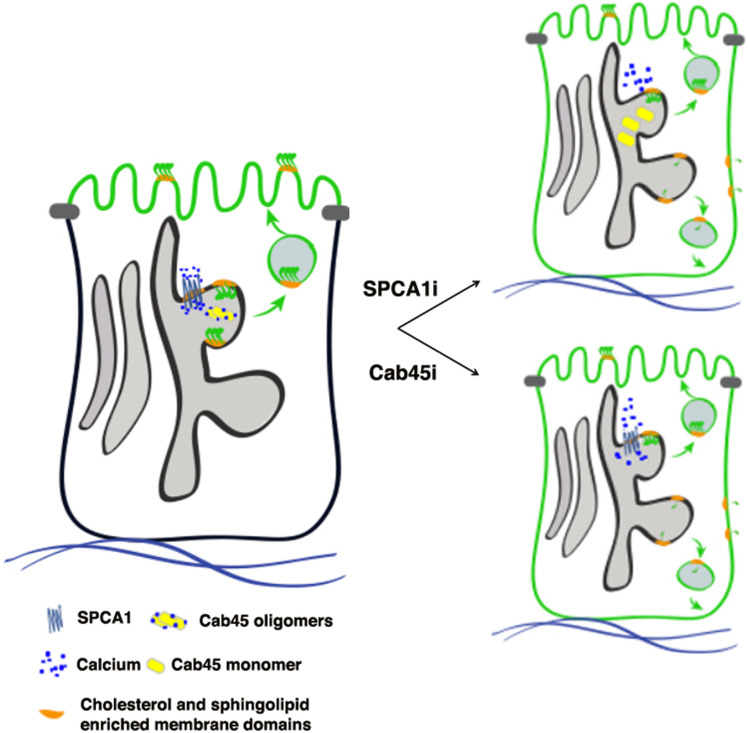
Fig. 8.
Model of GPI-AP clustering and sorting in MDCK cells. The scheme depicts the role of calcium in the Golgi clustering of GPI-APs (for simplicity, only one GPI-AP is shown). A GPI-AP oligomerizes (forming a homocluster) after its association to lipid microdomains in the medial Golgi. The Golgi homoclustering regulates apical sorting of GPI-APs. Calcium uptake in the TGN, governed by SPCA1, is essential for GPI-AP clustering. In control cells, SPCA1 allows the uptake of calcium within the Golgi that would lead to oligomerization of Cab45, which in turn stabilizes GPI-AP clustering and apical sorting. Upon SPCA1 knockdown, less calcium is uptaken by the Golgi, leading to the impairment of GPI-AP clustering that results in their missorting. Similarly, upon Cab45 knockdown, Golgi GPI-AP clustering is impaired, leading to their basolateral missorting.