Fig. 6.
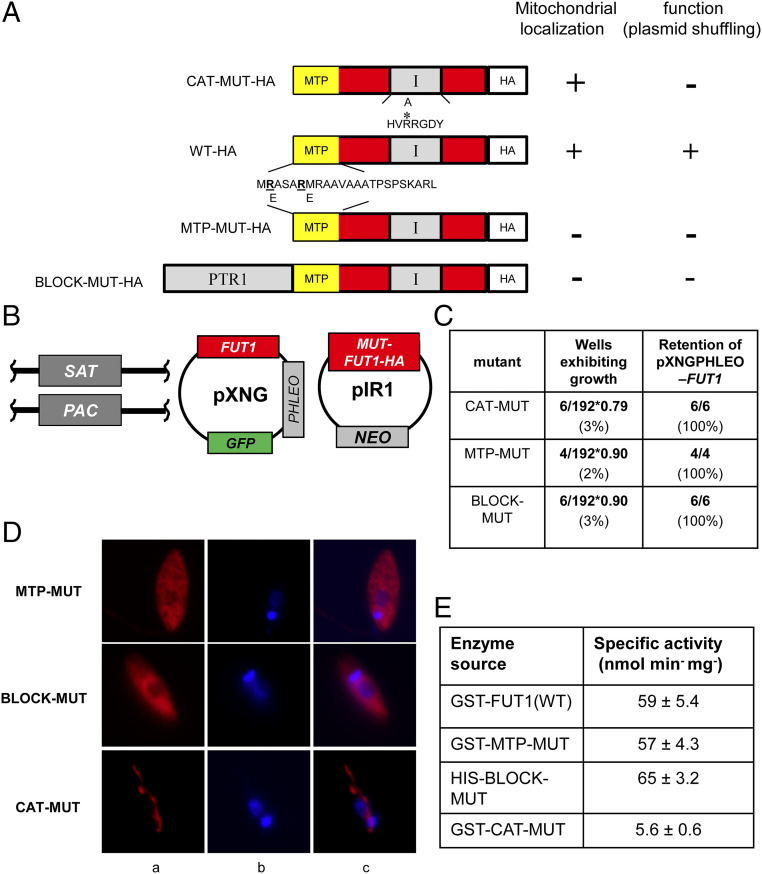
Both mitochondrial localization and fucosyltransferase activity are required for the essential function of FUT1. (A) Depiction of mutant LmjFUT1-HA designed to block mitochondrial import or catalysis. The predicted MTP is shown in yellow, the catalytic motif I is shown in gray, and the HA tag is shown in white, with the remainder of FUT1 in red. CAT-MUT-HA has an R297A substitution; MTP-MUT-HA replaces two Glu residues in the MTP with Arg; BLOCK-MUT-HA has the cytoplasmic protein PTR1 fused to the N terminus. The results of mitochondrial localization tests (D) and plasmid shuffling tests (C) are summarized on the Right of the illustrations. (B) Scheme of plasmid shuffling to test the function of mutant FUT1s. HA-tagged mutant FUT1s were expressed from pIR1NEO in the Δfut1−/+pXNGPHLEO-FUT1 line. Growth in the absence of phleomycin and FACS sorting of dim and bright cells was performed as in Fig. 2. (C) Plasmid shuffling tests of FUT1 mutants. Δfut1−pXNG-FUT1/pIR-MUT-HA lines was grown for 24 h in the absence of phleomycin, and analyzed by GFP flow cytometry. In all tests, survival of bright (control) cells was 79–90%. The results show that few dim cells yielded growth, and all of those arose from incomplete sorting (retention of pXNGPHLEO-FUT1). (D) Indirect immunofluorescence of HA-tagged FUT1 expressed from pIRNEO in the Δfut1−/+pXNGPHLEO-FUT1 background. Column a, anti-HA (red); column b, DNA (Hoechst, blue); and column c, merge of columns a and b. (E) Acceptor-dependent specific activity of purified recombinant FUT1 proteins assayed by GDP formation in the presence of GDP-Fucose and LNB. The average and SD of three preparations are shown.