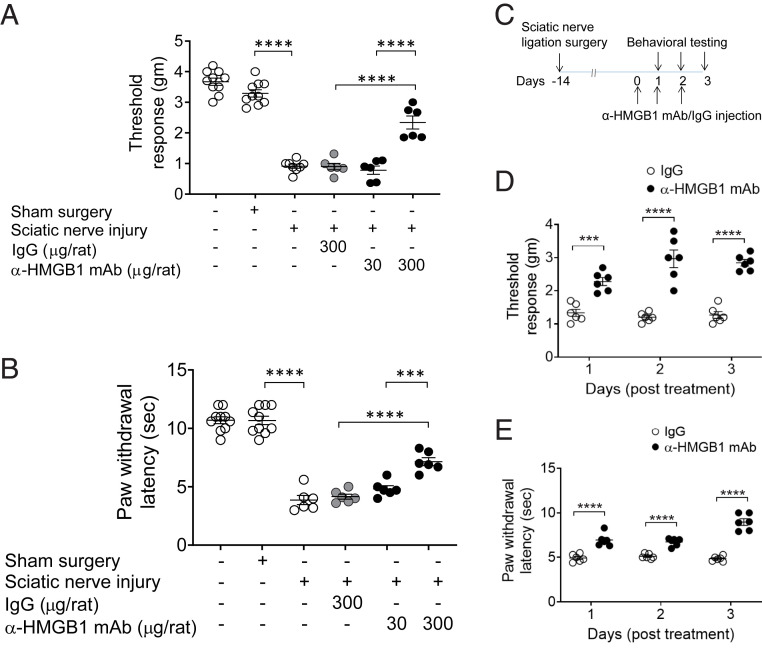
Fig. 3.
Anti-HMGB1 mAb administration ameliorates sciatic nerve injury–induced hyperalgesia. (A and B) Female Wistar rats were subjected to sciatic nerve ligation surgery or sham surgery 2 wk prior to i.p. administration of anti-HMGB1 mAb (30 or 300 µg per rat) or control IgG (300 µg per rat). (A) Mechanical (von Frey) and (B) thermal (Hargreaves) hypersensitivity were assessed at 6 h after antibody was administered. Dose-dependent improvement in mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity is observed after anti-HMGB1 mAb administration. Data are represented as individual mouse data points with mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test between groups: ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. n = 10 per group (normal or sham) and n = 6 (sciatic nerve injury). (C–E) Repetitive administration of anti-HMGB1 mAb ameliorates sciatic nerve injury–induced hyperalgesia. (C) Two weeks postsciatic nerve ligation or sham surgery, female Wistar rats received anti-HMGB1 mAb or IgG (300 µg/rat) i.p. once a day for 3 consecutive days. (D) Mechanical and (E) thermal hypersensitivity were assessed daily for 3 d after anti-HMGB1 mAb administration. Data are represented as individual mouse data points with mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test between groups: ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, n = 6 per group.