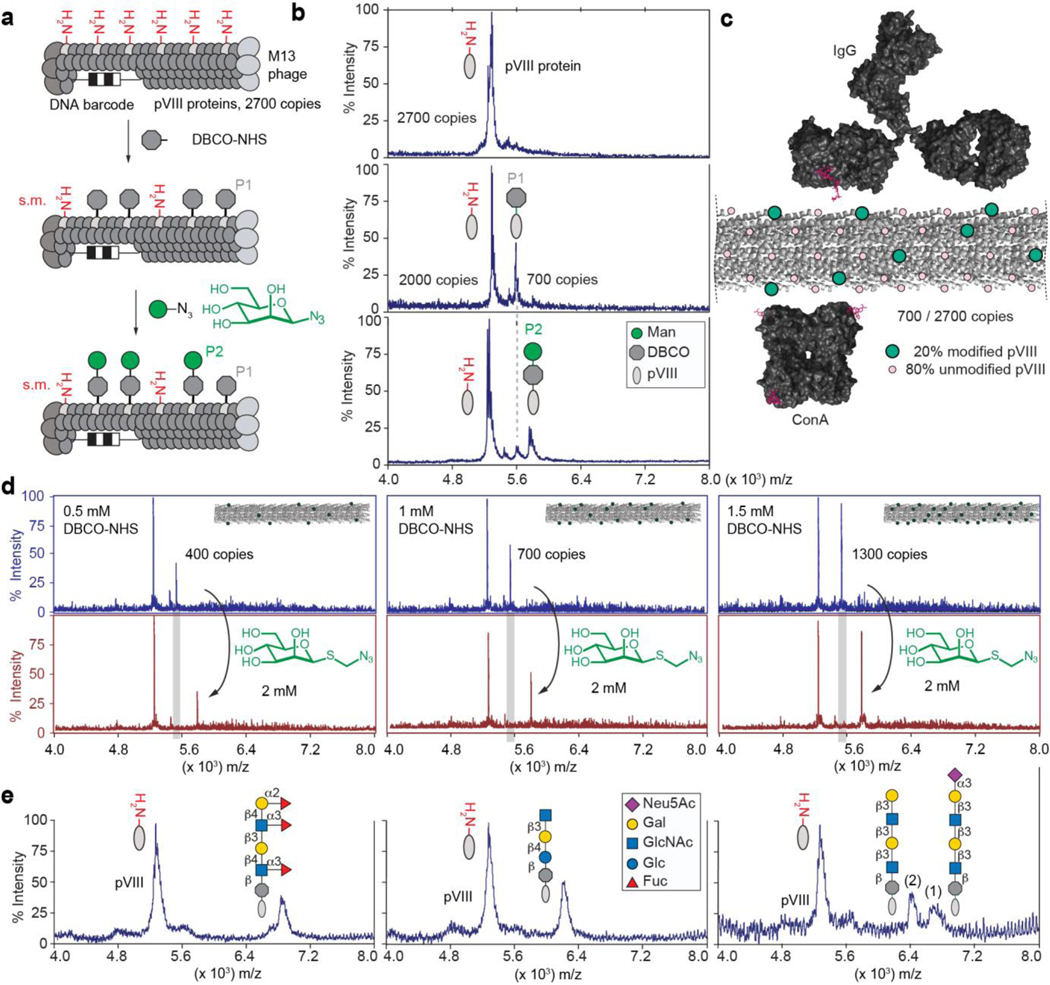
Fig. 1: Synthesis and characterization of LiGA components.
a, Representation of two-step chemical glycosylation of phage. b, MALDI mass spectrometry characterization of starting material (protein pVIII), alkyne-functionalized product (DBCO-pVIII, P1), and glycoconjugate product (P2). c, Spacing of glycans on M13 virion (PDB: 2MJZ and 2C0W) compared to spacing of binding sites of IgG antibody and lectin ConA. d, Control of the density of the modification by controlling the concentration of DBCO-NHS. Spectra in top panel represent before βMan addition and bottom panel shows after βMan addition. e, Representative spectra of chemical modification of coat protein pVIII with glycans of different structural complexity. In MALDI conditions, sialoglycans exhibited a loss of sialic acid during ionization in acidic matrix; therefore MALDI of phage particles decorated with glycans containing terminal Neu5Ac contained two peaks (intact glycoconjugate and that with cleaved Neu5Ac).