Figure 7. Site-specific MARylation of RPL24 at Glu4 inhibits polysome formation.
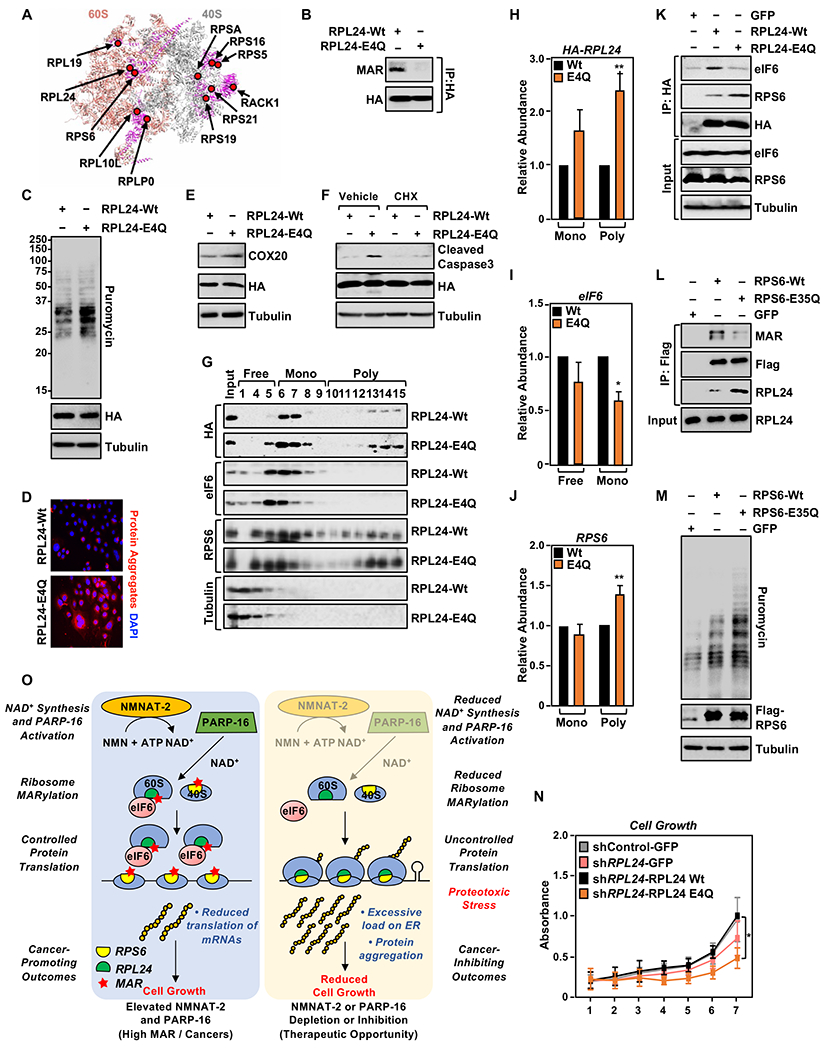
(A) Spatial distribution of the proteins modified by MARylation in the 80S ribosome (PDB ID: 4V6X). RPL24, which is located at the 60S-40S interface, is MARylated.
(B) RPL24 is MARylated at Glu 4. HA-tagged RPL24 was immunoprecipitated from OVCAR3 cells ectopically expressing wild-type (Wt) or MARylation deficient (E4Q) RPL24 and subjected to Western blotting for MAR and HA.
(C) RPL24-E4Q expression enhances protein synthesis in OVCAR3 cells. Western blot analysis of puromycin incorporation assays from OVCAR3 cells subjected to Dox-induced expression of RPL24.
(D) RPL24-E4Q expression promotes the accumulation of protein aggregates. Staining of protein aggregates using Proteostat aggresome detection reagent in OVCAR3 cells subjected to Dox-induced expression of RPL24.
(E) RPL24-E4Q expression enhances COX20 protein levels. Western blot analysis for COX20 in OVCAR3 cells subjected to Dox-induced expression of RPL24.
(F) Loss of RPL24 MARylation induces apoptosis. OVCAR3 cells subjected to Dox-induced expression of RPL24 were assayed for caspase 3 cleavage by Western blotting. Inhibition of translation by cycloheximide blocks the cleavage of caspase 3.
(G - J) Loss of RPL24 MARylation induces polysome formation. (G) Western blot analysis for HA-tagged RPL24, eIF6 and RPS6 of the sucrose density gradient fractions prepared from OVCAR3 cells subjected to Dox-induced expression of RPL24. Each bar in the graph in (H) represents the mean ± SEM of the relative abundance of RPL24, eIF6, and RPS6 in monosomes or polysomes (n = 4, Student’s t-test, * p < 0.05 and ** p<0.01).
(K) Loss of Glu4 MARylation inhibits RPL24 interaction with eIF6. HA-tagged RPL24 was immunoprecipitated from OVCAR3 cells with Dox-induced expression of RPL24 and subjected to Western blotting for eIF6, RPS6, and HA.
(L) MARylation of RPS6 at Glu 35 inhibits binding to RPL24. Flag-tagged RPS6 was immunoprecipitated from OVCAR3 cells subjected to Dox-induced expression of wild-type (Wt) or MARylation deficient (E35Q) RPS6 and subjected to Western blotting for MAR, RPL24 and Flag.
(M) RPS6-E35Q expression enhances protein synthesis in OVCAR3 cells. Western blot analysis of puromycin incorporation assays from OVCAR3 cells subjected to Dox-induced expression of RPS6.
(N) RPL24-E4Q expression inhibits cell growth. OVCAR3 cells subjected to Dox-induced knockdown and re-expression of RPL24 for 7 days and crystal violet staining was performed, (n = 4, one-way ANOVA, * p < 0.01).
(O) Schematic of the mechanisms by which NMNAT-2/NAD+ and PARP-16/MAR regulate protein homeostasis and ovarian cancer growth. Additional details are provided in the text.
