Figure 3. Identification of critical positions of NPR-1 for receptor activation and contact points to the ligand FLP-21.
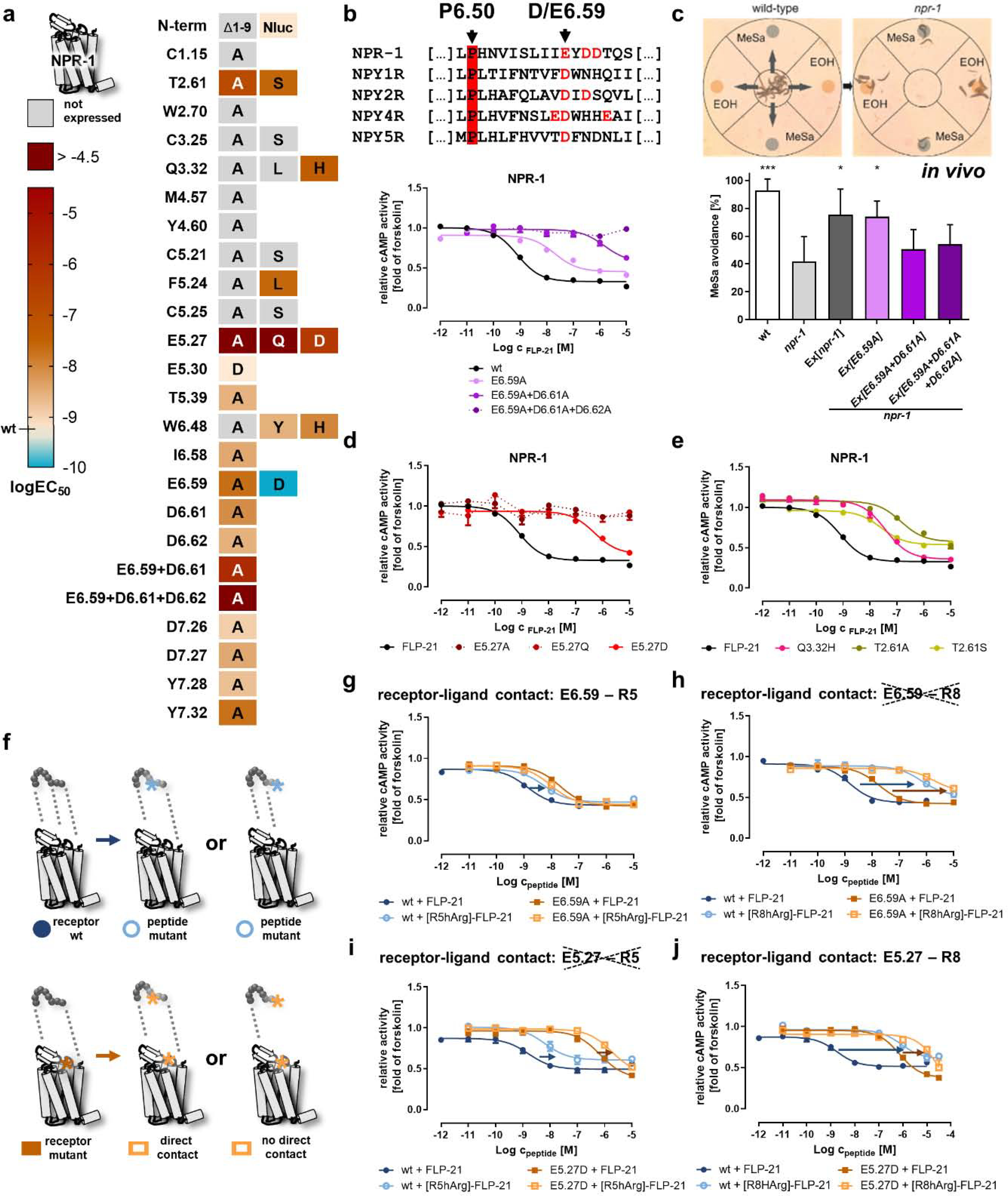
a) Activity of NPR-1 variants depicted as heatmap. The logEC50 values were determined in a cAMP reporter gene assay (Gi/o), and are color-coded from light orange (wild type, high potency) to dark red (logEC50 > −5). A gain of function is indicated by cyan color. The nomenclature of the receptor positions follows Ballesteros und Weinstein [55]. “Not expressed” indicates receptor variants that are not correctly folded and transported to the plasma membrane (cf. SI: Figure S1). Selected concentration-response curves are shown in panels b, d, e. b) Alignment of TM6/ECL3 residues of NPR-1 with the human NPY receptors. A cluster of acidic residues in NPR-1 is shown in red, and the conserved D/E6.59 is indicated by an arrow. Mutation of this acidic cluster gradually decreases receptor activity. c) The acidic cluster in TM6/ECL3 is also critical for receptor function in vivo in C. elegans. This is measured by phenotypic rescue of a npr-1 null mutant in a methyl salicylate (MeSa) avoidance assay (see methods for details). npr-1 deficient animals lose MeSa avoidance, which is rescued by transgenic expression of npr-1 driven by a npr-1 promoter (Ex[npr-1]). The single exchange of E6.59 to alanine in NPR-1 still gives sufficient receptor activity for a phenotypic rescue (Ex[E6.59A]), while the combination mutants Ex[E6.59A+D6.61A] and Ex[E6.59A+D6.61A+D6.62A] are indistinguishable from the npr-1 null mutant. Data are shown as mean ± SD of n ≥ 4 independent experiments (N ≥ 60 worms in each experiment). *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001 compared to the npr-1 null mutant. d) The receptor position E5.27 in ECL2 is highly important for receptor activation and even a very mild mutation (E5.27D) leads to a drastic EC50 shift of > 400-fold, while exchanges to glutamine or alanine are expressed, but not activatable up to peptide concentrations of 10 μM. e) In addition to the two acidic clusters in TM6 and ECL2, mutation of two hydrophilic positions T2.61 and Q3.32 decreases receptor activation by > 30-fold. f) Double-cycle mutagenesis to find interacting residues between NPR-1 and FLP-21. Mutation of a functionally important ligand position eliminates one binding interaction (light blue) compared to the wild type situation (dark blue), which leads to a decreased receptor activity (first round; upper panel). In the second round (lower panel), the receptor is mutated (light orange). If the two tested positions interact, this will not further affect the receptor activity, as the corresponding interaction had been eliminated by the peptide mutation before (lower panel, middle). In contrast, if the receptor mutation does not interact with the tested ligand position, the receptor activity is further decreased (lower panel, right). g/h/i/j) Receptor positions E6.59 and E5.27 were tested against [R5/8]-FLP-21 mutants. EC50 shifts are indicated with arrows (blue/orange). A reduced shift and thus a direct interaction (smaller orange arrow compared to blue arrow) was found for [R5A]-FLP-21 to E6.59A and for [R8hArg]-FLP-21 to E5.27D, but not for the other combinations. b, d, e, g-j: Data represent x-fold of forskolin (mean ± SEM) of n ≥ 3 independent experiments.
