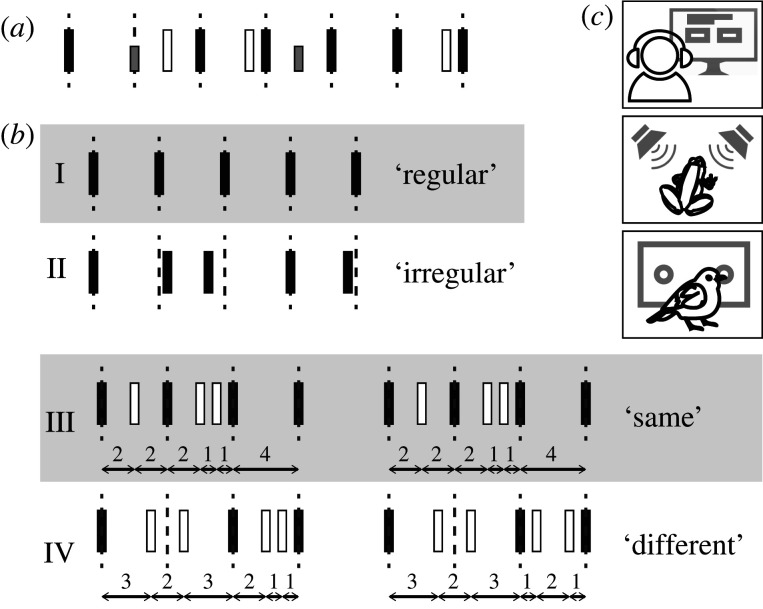
Figure 2.
Rhythm perception tasks. (a) In implicit tasks, participants perform a task unrelated to the rhythm, such as detecting intensity changes. Performance is associated with the rhythmic structure, with better performance in more salient metrical positions. (b) In explicit tasks, participants may, for example, discriminate between different categories of rhythms (I and II), or may judge whether two rhythmic patterns are the same (III) or different (IV). (c) Variants of perceptual tasks have been done both in humans and non-human animals. For example, frogs' mating preferences, measured as approach to a stimulus, can be used as a proxy for discrimination performance, and birds can be trained in 2AFC tasks.