FIGURE 1.
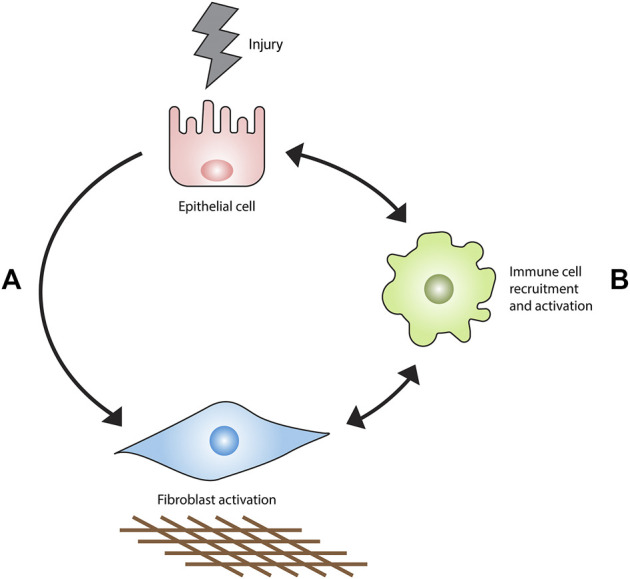
Current model of IPF pathogenesis. Epithelial injury results in fibrosis primarily through an interaction with fibroblasts (A) rather than the recruitment and activation of immune cell populations (B). Immune cells accumulate in the injured lung and orchestrate the development, maintenance, progression or regression of fibrosis.
