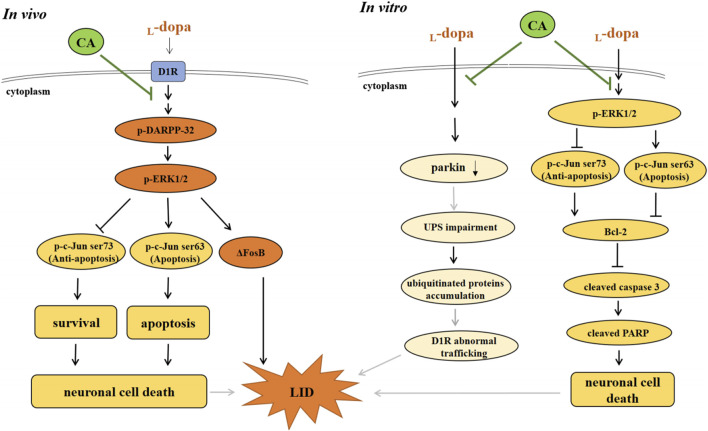
FIGURE 9.
The actions of neuroprotective mechanism of CA on LID in in vivo and in vitro studies. (A) In in vivo study, L-dopa stimulates DIR protein, and then activates the phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and ERK1/2, which elevates ΔFosB protein, leading to develop the LID in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Moreover, L-dopa administration induced neuronal cell death through regulating ERK1/2-c-Jun pathway. However, CA alleviates these effects induced by L-dopa. (B) In in vitro study, pretreatment of CA with SH-SY5Y cells attenuates L-dopa-triggered apoptotic cell death mediated via increasing c-Jun ser73 activation and decreasing c-Jun ser63 activation by ERK1/2. Additionally, CA could be improved the development of LID is related to the induction of parkin protein, leading to prevent the ubiquitinated protein accumulation and D1R abnormal trafficking (gray line).