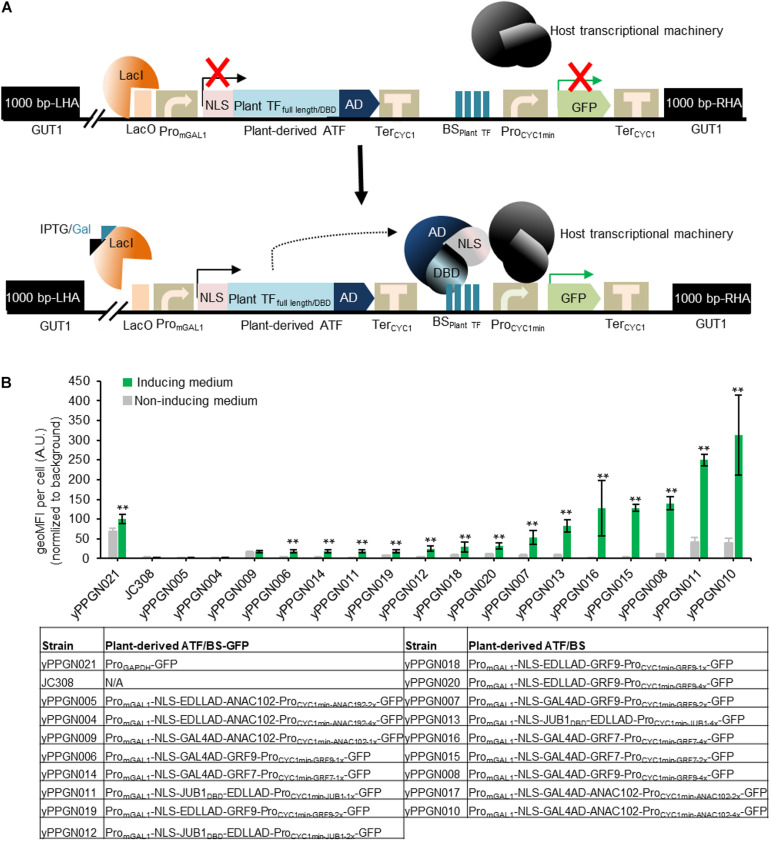
FIGURE 2.
Library of genome-integrated, plant-based ATF/BSs in P. pastoris. (A) Schematic overview of plant-derived ATFs and BSs used in the present study. The ATF cassette contains an mGAL1 promoter with a lacO site at the 5′ end (induced by IPTG and galactose), NLS, and full-length plant TFs or their DBDs fused in different combinations with GAL4AD or EDLLAD and TerCYC1. The transactivation capacity of the ATFs was tested against the TF BSs inserted as one (1x), two (2x), or (4x) copies upstream of the CYC1 minimal promoter driving GFP reporter expression. The 1,000-bp LHA and RHA allow integration of the regulator cassette into the GUT1 sites of the genome. The expression of ATFs was controlled by an IPTG-inducible GAL1 promoter. Constitutive expression of the repressor (LacI) inhibits the expression of plant-derived ATFs, while the addition of inducers (IPTG and galactose) results in ATF expression. Binding of the ATF to its cognate BS within the CYC1 minimal promoter drives GFP expression. Fluorescence output is measured in the absence and presence of inducer. AD, activation domain; ATF, artificial transcription factor; BSplant TF, binding site of the plant transcription factor; BS, binding site; DBD, DNA binding domain; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IPTG, isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside; GUT1, glycerol utilization 1; LHA, left homology arm; NLS, nucleus localization signal; ProminCYC1, minimal CYC1 promoter; PromGAL1, modified GAL1 promoter carry LacO site; LacI, Lac repressor; TerCYC1, CYC1 terminator; RHA, right homology arm. (B) Transcriptional output of plant-derived ATF/BSs in P. pastoris. The GFP output was tested in the absence and presence of IPTG and galactose. The types of ATF used to generate yPPGN004—yPPGN020 strains are listed in the table. P. pastoris strain yPPGN021 was used as a positive control, where the GFP expression is controlled by GAPDH promoter allowing constitutive expression of GFP in both inducing- and non-inducing medium. EDLLAD, activation domain from plant; GAL4, GAL4 activation domain of yeast; GRF7 and GRF9, Growth-Regulating Factor 7 and 9; JUB1, NAC TF JUNGBRUNNEN1; ANAC102, A NAC TF 102; VP64AD, viral activation domain. Gray, non-induction medium; green, induction medium. Data are expressed as the geometric mean ± SD of the fluorescence intensity obtained from three cultures, each derived from an independent yeast colony and determined in three technical replicates. Data are normalized to the average geoMFI of the background fluorescence obtained from the wild-type JC308 strain (Lin Cereghinoa et al., 2001). Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference from the non-induction medium (Student’s t-test; **p < 0.01). AU, arbitrary units; geoMFI, geometric mean fluorescence. The full data are shown in Supplementary Data 1.